Hi,
DSX solves your toughest data challenges with the best tools and the latest expertise in a social environment built by data scientists.
And in order to use CPLEX we can use the DOCPLEX Python API
But that means we use a General Programming Language in order to model.
Some prefer to use an Algebraic Modeling Language like OPL for that part as discussed at https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/optimization-aka-prescriptive-analytics-should-we-write-fleischer
On a given computer, we can call OPL from Python through oplrun as said at
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/community/forums/html/topic?id=0b6cacbe-4dda-4da9-9282-f527c3464f47&ps=25
and http://www.opalytics.com/2017/06/rapid-deployment-optimization-developed-opl/
But how can we call OPL from DSX ?
Let me tell you ...
As an example I will call blending.mod and blending.dat from DSX.
1) You upload the .mod and the .dat to DSX notebook
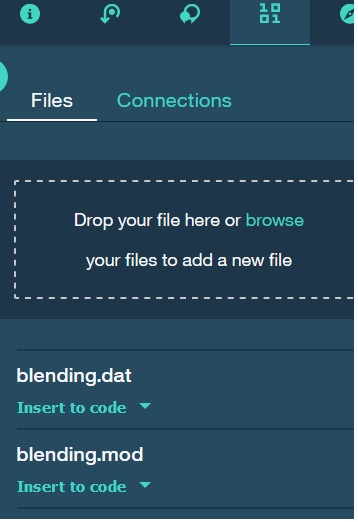
and from there "Insert to code" will generate some python code that you will add in your notebook:
This will look like
# Your data file was loaded into a StringIO object and you can process the data.
# Please read the documentation of pandas to learn more about your possibilities to load your data.
# pandas documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/io.html
data_1 = get_object_storage_file_with_credentials_('DefaultProject__', 'blending.mod')
data_2 = get_object_storage_file_with_credentials_('DefaultProject__', 'blending.dat')
2) You give your credentials and change
url = None
key = None
into your own
3) The call
ctx = Context.make_default_context(url=url, key=key)
#ctx.solver.docloud.print_information()
from docplex.mp.environment import Environment
env = Environment()
from docloud.job import JobClient
client = JobClient(url, key)
print(data_1.getvalue())
print(data_2.getvalue())
file_object = open("blending.mod","w")
file_object.write(data_1.getvalue())
file_object.close();
file_object2 = open("blending.dat","w")
file_object2.write(data_2.getvalue())
file_object2.close();
with open("blending.mod", "rb") as modFile:
with open("blending.dat", "rb") as datFile:
resp = client.execute(input = [{ 'name' : 'blending.mod', 'file' : modFile },{'name' : 'blending.dat', 'file' : datFile}],
output = "results.json",
log = "solver.log",
gzip = True,
waittime= 300,
delete_on_completion=True)
file = open("solver.log", "r")
for line in file:
print (line,);
print("resp=",resp)
which gives
[2017-09-17T10:48:58Z, INFO] Total time spent in post processing: 5 msecs.
[2017-09-17T10:48:58Z, INFO] Solve finished with status: OPTIMAL_SOLUTION.
resp= <docloud.job.JobResponse object at 0x7f942dfcccc0>
This could ease the job of data science experience users who will want to add optimization to what they do.
regards
Alex Fleischer
PS:
Many how to with OPL at https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/how-opl-alex-fleischer/
Many examples from a very good book : https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/model-building-oplcplex-alex-fleischer/
Making optimization simple : https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/making-decision-optimization-simple-alex-fleischer/
#DecisionOptimization#OPLusingCPLEXOptimizer