Topics
- Transforming data to create a Use Map Table
- Lookupex vs Tablematch
- Collapse Grid by Transformation
- Manage Unique Row Filter
- Utilizing Metafields
Use Map Table
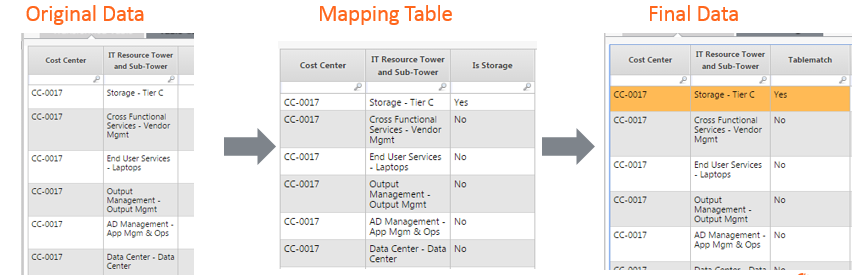
What is a Use Map Table?
An allocation strategy that utilizes data relationships that exists in a table to create a connection between two objects without using the Apptio Inference Engine
How to create a Use Map Table:
Three columns needed:
- Unique Identifier of Sending Object
- Unique Identifier of Receiving Object
- Weight for allocation
How to create a Use Map Table allocation in the model:
- Click the allocation line
- Select “Advanced” under the “Allocation” section
- Click “Click to Specify”
- The formula is as follows:
=USE_MAP_TABLE({Table Name}:{Weighting Value}, {Unique Identifier for Sending Object}, {Unique Identifier for Receiving Object}, ratio)
Lookupex vs Tablematch
LookupEx
- LookupEx is the same as Lookup, except that LookupEx returns values for all matches rather than just the last one.
- Does not work with preview box
- Can only have one per dataset
- Will duplicate rows for all returned values
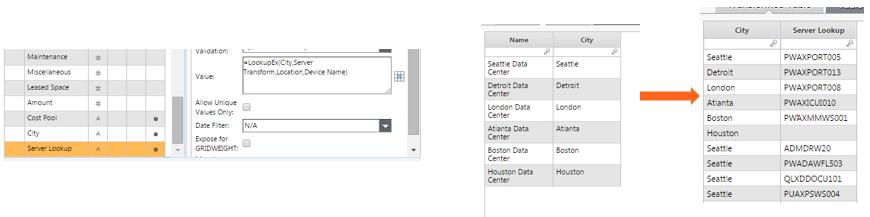
Tablematch
- Used to create complex IF statements using a table-based format.
- Supports text and numbers.
- Only returns the first value, like a Lookup, but will not return {Various}
When to use a LookupEx:
- The LookupEx function should be used in Apptio when trying to add a column from another dataset that returns multiple values based on the matching column
- Limited to the criteria/granularity specified in the index column of the data
- Can return multiple values and duplicates rows to accommodate all return values
When to use a Tablematch:
- Tablematch should be used when trying to add a column or multiple columns from another dataset based on multiple column criteria
- Can utilize many columns to bring back a value
- Only returns one value, if there are multiple in the Tablematch table then it will return the first value
Collapse Grid by Transformation
What is Collapse Grid By?
- A function in Apptio that allows the user to collapse columns into rows, essentially pivoting the data
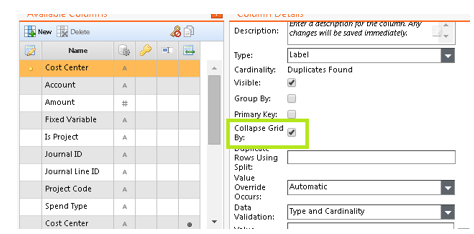
When to use a Collapse Grid By
- When trying to reformat data that is split into multiple columns into rows
- For pivoting Cost Center by IT Resource Towers where the IT Resource Towers are set up as columns in the data
- For Date filtering in Annual files with more than one numerical value
Manage Unique Row Filter
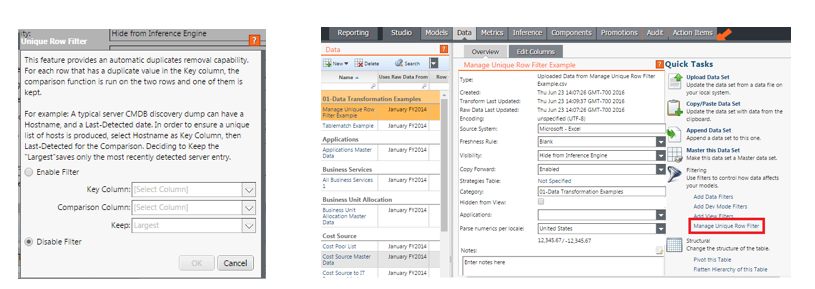
What is Manage Unique Row Filter?
- A function in Apptio that allows the user to filter out duplicate rows of data
Utilizing Metafields
What is a Metafield?
- Columns included in Master Datasets that allow for increased granularity for objects
Why do Metafields matter?
- Allow for increased granularity in keys without breaking upgradability
Where can I find Metafields?
- In Out of the Box Master Datasets
Topics
- Database Relationships
- How to Document Data Sets with the Notes Field
- Data Versioning
- From Data to Calculated Metrics
- Additional Data Cleanliness Content
Database Relationships
What is a relational database?
- When data is stored in different data sets you rely on relationships between the tables to pull the data together in meaningful ways.
- Relationships are drawn between data sets through the use of “keys”.
Keys
- A key is a data point that is shared between two data sets that allows a link to be drawn between them.
- Apptio does not use Primary Keys (PK) the way that other relational databases do. In Apptio a key is used to link data sets, a PK is used as a unique identifier for each row in the data.
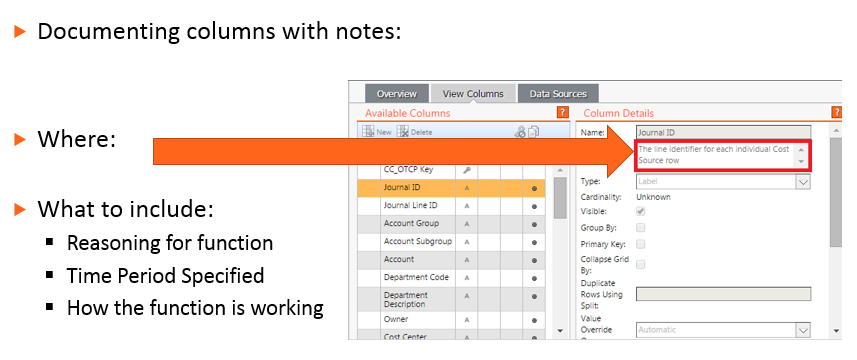
Documenting Data Sets with Notes
Key Items for Notes:
- Any Value Overrides to raw columns
- Filters to dataset
- Transforms created from the dataset/appended to the dataset
- Advanced modifications to the data
Versioning Data
What does it mean to version data
- This is the replacement or modification of a data set or transform in a time period other than the original period.
- Both raw data and transformed data can be versioned in Apptio
- Raw data is versioned by loading a file in a new time period replacing the previous data
- Transformed data is versioned by unlocking and editing the transform in a new time period
How do you identify versioned data
- Versioned data is identified by looking at the “Uses Raw Data From” column in the data tab of Apptio Studio. If the time period for the data is different than the start date of the project when data was originally loaded and transforms created, the data is likely versioned.
From Data to Calculated Metrics
How do metrics use data?
- Report numeric values
- Mathematical calculation against numeric values
- Formulas and functions referencing both numeric and non-numeric values
Building metrics
- Best Practice: Data used in metrics should be exposed to the inference engine
- You must reference the complete table name and column name in the format “table.column”
- The metric type default is “calculated” and should not be changed for this scenario
Additional Data Cleanliness Items
Naming conventions:
- Don’t include symbols in column headers (*, &, -, etc.)
- Use ATUM taxonomy wherever possible
- Stay consistent with column headers over time
- Source columns
- Naming transforms
- Dataset can be clearly identified by name
- Change column type in raw data (ex: from Number to Label)
Process improvement for data cleanliness
- Make desired fields required so you get the data you want (and need) – this includes adding new fields
- For fields that should have a limited number of answers or specific types of entry (i.e. numeric) set a limited number of potential entries via dropdown or other logic if possible
Apptio best practices
- Use categories to organize your data
- Delete unused data sets
- Minimize transforms of transforms except where needed for order of operations
- Only version data when you are making a major change (i.e. a new GL system, org changes, etc.)