IBM Storage Ceph Object Storage Multisite Replication Series. Part Two
In the previous episode, we introduced IBM Storage Ceph Object Storage multisite features. We described the lab setup we will use in the following chapters to deploy and configure IBM Storage Ceph object multisite asynchronous replication. Here is a Link to the initial blog.
Part two of this series will enumerate the steps to establish the initial multisite replication between our Ceph clusters, as depicted in the following diagram.
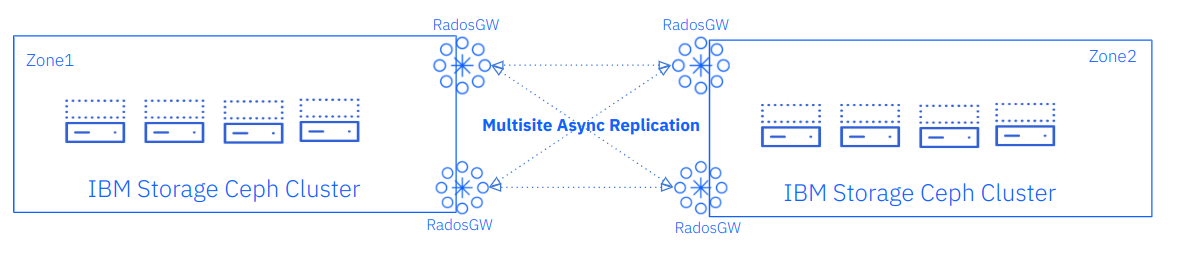
IBM Storage Ceph Object Storage Multisite Initial Configuration
As part of the IBM Storage Ceph 6.1 release, a new MGR module called RGW was added to the ceph orchestrator “cephadm”. The rgw manager module makes the configuration of Multisite Replication straightforward. This section will show you how to configure IBM Storage Ceph Object Storage multisite replication between 2 zones (each zone is an independent Ceph cluster) through the CLI using the new rgw manager module.
We will start by creating an RGW module spec file for cluster1.
We will use labels on our hosts to help define which nodes each service should run on; in this case, for the replication rgw services, we are setting the “rgwsync” label. Any host that has this label configured will start an rgw service with the specs defined in the file. The rest of the options included will take care of configuring the names for our realm, zone group and zone, and we also want the rgw services to listen on port 8000.
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# cat << EOF >> /root/rgw.spec
placement:
label: rgwsync
count_per_host: 1
rgw_realm: multisite
rgw_zone: zone1
rgw_zonegroup: multizg
spec:
rgw_frontend_port: 8000
EOF
In our first cluster, we are going to run the sync rgw services on nodes ceph-node-00 and ceph-node-01, so we need to label the corresponding nodes:
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# ceph orch host label add ceph-node-00.cephlab.com rgwsync
Added label rgwsync to host ceph-node-00.cephlab.com
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# ceph orch host label add ceph-node-01.cephlab.com rgwsync
Added label rgwsync to host ceph-node-01.cephlab.com
Once the nodes have been labeled, we can enable the rgw manager module and bootstrap the rgw multisite configuration; when bootstrapping the multisite config, the rgw manager module is going to take care of the following steps:
- Create the realm, zone group, and zone and apply the period.
- Specific rgw rados pools with the name of the zone get created.
- Create an rgw multisite replication sync user
- Configure the realm, zone group, and zone for each rgw service and the ceph level(ceph config)
- Create the rgw services(using the cephadm orchestrator)
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# ceph mgr module enable rgw
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# ceph rgw realm bootstrap -i rgw.spec
Realm(s) created correctly. Please use 'ceph rgw realm tokens' to get the token.
Let’s check the realm:
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# radosgw-admin realm list
{
"default_info": "d85b6eef-2285-4072-8407-35e2ea7a17a2",
"realms": [
"multisite"
]
}
Multisite sync user:
[root@ceph01 ~]# radosgw-admin user list | grep sysuser
"Sysuser-multisite"
Zone1 rgw rados pools:
[root@ceph01 ~]# ceph osd lspools | grep rgw
24 .rgw.root
25 zone1.rgw.log
26 zone1.rgw.control
27 zone1.rgw.meta
Once we create the first bucket, the bucket index pool will be created automatically. Also, once we upload the first objects/data to a bucket in zone1, the data pool will be created for us. By default pools with a replica scheme of three are created using the cluster pre-defined crush rule: “replicated_rule”; if we want to use EC pools for the data pool, or customise, for example, the failure_domain, we need to manually pre-create the pools with our customisations before we start uploading data into the first bucket, there is an example of how to do this operation through the Dashboard UI in the first chapter of the this IBM Ceph Redbook.
NOTE: Don’t forget to double-check that your rgw pools have the right amount of PGs to provide the required performance; we can choose to enable the PG autoscaler manager module or statically calculate the amount of PGs our pools are going to need upfront with the help of the PG calculator.
NOTE: Only the rgw data pool can be configured with an EC replica scheme; the rest of the pools need to be configured with a replication scheme, like, for example, replica 3.
The rgw services are up and running service the S3 endpoint on port 8000:
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# curl http://ceph-node-00:8000
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><ListAllMyBucketsResult xmlns="http://s3.amazonaws.com/doc/2006-03-01/"><Owner><ID>anonymous</ID><DisplayName></DisplayName></Owner><Buckets></Buckets></ListAllMyBucketsResult>
The rgw manager module creates a token with encoded information of our deployment; other Ceph clusters that want to be added as a replicated zone to our multisite configuration can import this token into the rgw manager module and get replication configured and running with a single command.
We can check the contents of the token; we can retrieve the token with the `ceph rgw realm tokens` command and decode it with the `base64` command; as you can see, it provides the required information for the secondary zone to connect to the primary zone group and pull the realm and zone group configuration.
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# TOKEN=$(ceph rgw realm tokens | jq .[0].token | sed 's/"//g')
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# echo $TOKEN | base64 -d
{
"realm_name": "multisite",
"realm_id": "d85b6eef-2285-4072-8407-35e2ea7a17a2",
"endpoint": "http://ceph-node-00.cephlab.com:8000",
"access_key": "RUB7U4C6CCOMG3EM9QGF",
"secret": "vg8XFPehb21Y8oUMB9RS0XXXXH2E1qIDIhZzpC"
}
You can see from the prompt that we have switched to our second Ceph cluster; we have copied the token from our first cluster and defined the rest of the parameters similarly to cluster 1.
[root@ceph-node-04 ~]# cat rgw2.spec
placement:
label: rgwsync
count_per_host: 1
rgw_zone: zone2
rgw_realm_token: ewogICAgInJlYWxtX25hbWUiOiAibXVsdGlzaXRlIiwKICAgICJyZWFsbV9pZCI6ICIxNmM3OGJkMS0xOTIwLTRlMjMtOGM3Yi1lYmYxNWQ5ODI0NTgiLAogICAgImVuZHBvaW50IjogImh0dHA6Ly9jZXBoLW5vZGUtMDEuY2VwaGxhYi5jb206ODAwMCIsCiAgICAiYWNjZXNzX2tleSI6ICIwOFlXQ0NTNzEzUU9LN0pQQzFRUSIsCiAgICAic2VjcmV0IjogImZUZGlmTXpDUldaSXgwajI0ZEw4VGppRUFtOHpRdE01ZGNScXEyTjYiCn0=
spec:
rgw_frontend_port: 8000
We label the hosts that will run the ceph sync radosgw services:
[root@ceph-node-04 ~]# ceph orch host label add ceph-node-04.cephlab.com rgwsync
Added label rgwsync to host ceph-node-04.cephlab.com
[root@ceph-node-04 ~]# ceph orch host label add ceph-node-05.cephlab.com rgwsync
Added label rgwsync to host ceph-node-05.cephlab.com
Enable the module, and run the `ceph rgw zone create ` command with the spec file we created a moment ago:
[root@ceph02 ~]# ceph mgr module enable rgw
[root@ceph02 ~]# ceph rgw zone create -i rgw2.spec --start-radosgw
Zones zone2 created successfully
The rgw manager module will take care of pulling the realm and zone group periods using the access and secret key from the multisite sync user; finally, it will create zone2 and do a final period update so all zones have the latest configuration changes in place with zone2 added to zone group multizg, in the following output from the “radosgw-admin zonegroup get” command we can see the zone group endpoints, we can see that zone1 is the master zone for our zone group, and the corresponding endpoints for zone1 and zone2.
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# radosgw-admin zonegroup get
{
"id": "2761ad42-fd71-4170-87c6-74c20dd1e334",
"name": "multizg",
"api_name": "multizg",
"is_master": true,
"endpoints": [
"http://ceph-node-04.cephlab.com:8000",
"http://ceph-node-05.cephlab.com:8000"
],
"hostnames": [],
"hostnames_s3website": [],
"master_zone": "66df8c0a-c67d-4bd7-9975-bc02a549f13e",
"zones": [
{
"id": "66df8c0a-c67d-4bd7-9975-bc02a549f13e",
"name": "zone1",
"endpoints": [
"http://ceph-node-00.cephlab.com:8000",
"http://ceph-node-01.cephlab.com:8000"
],
"log_meta": false,
"log_data": true,
"bucket_index_max_shards": 11,
"read_only": false,
"tier_type": "",
"sync_from_all": true,
"sync_from": [],
"redirect_zone": "",
"supported_features": [
"compress-encrypted",
"resharding"
]
},
{
"id": "7b9273a9-eb59-413d-a465-3029664c73d7",
"name": "zone2",
"endpoints": [
"http://ceph-node-04.cephlab.com:8000",
"http://ceph-node-05.cephlab.com:8000"
],
"log_meta": false,
"log_data": true,
"bucket_index_max_shards": 11,
"read_only": false,
"tier_type": "",
"sync_from_all": true,
"sync_from": [],
"redirect_zone": "",
"supported_features": [
"compress-encrypted",
"resharding"
]
}
],
"placement_targets": [
{
"name": "default-placement",
"tags": [],
"storage_classes": [
"STANDARD"
]
}
],
"default_placement": "default-placement",
"realm_id": "beeea955-8341-41cc-a046-46de2d5ddeb9",
"sync_policy": {
"groups": []
},
"enabled_features": [
"resharding"
]
}
If we want to verify that the replication is working, Let’s create a user and a bucket:
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# radosgw-admin user create --uid='user1' --display-name='First User' --access-key='S3user1' --secret-key='S3user1key'
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [None]: S3user1
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: S3user1key
Default region name [None]: multizg
Default output format [None]: json
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# aws --endpoint http://s3.cephlab.com:80 s3 ls
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# aws --endpoint http://s3.cephlab.com:80 s3 mb s3://firstbucket
make_bucket: firstbucket
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# aws --endpoint http://s3.cephlab.com:80 s3 cp /etc/hosts s3://firstbucket
upload: ../etc/hosts to s3://firstbucket/hosts
If we check from our second Ceph cluster, zone2, we can see that all the metadata has been replicated, and all the users and buckets that we created in zone1 are now present in zone2
NOTE: In this example, we will use the radosgw-admin command to check, but we could also use the S3 API commands pointing the AWS client to the IP/hostname of an rgw on the second zone.
[root@ceph-node-04 ~]# radosgw-admin user list
[
"dashboard",
"user1",
"sysuser-multisite"
]
[root@ceph-node-04 ~]# radosgw-admin bucket stats --bucket testbucket | jq .bucket
"testbucket"
To check the status of the replication, we can use the `radosgw-admin sync status` command, for example:
[root@ceph-node-00 ~]# radosgw-admin sync status
realm beeea955-8341-41cc-a046-46de2d5ddeb9 (multisite)
zonegroup 2761ad42-fd71-4170-87c6-74c20dd1e334 (multizg)
zone 66df8c0a-c67d-4bd7-9975-bc02a549f13e (zone1)
current time 2024-01-05T22:51:17Z
zonegroup features enabled: resharding
disabled: compress-encrypted
metadata sync no sync (zone is master)
data sync source: 7b9273a9-eb59-413d-a465-3029664c73d7 (zone2)
syncing
full sync: 0/128 shards
incremental sync: 128/128 shards
data is caught up with source
Summary & up next
As a recap, in Part Two of this multisite series, we have gone through the steps of deploying IBM Storage Ceph Object Storage multisite replication between two sites/zones using the RGW manager module; this is just our first building block as our target is to have a full-blown deployment including the much-needed load-balancers.
In Part Three of the series we will continue fine tuning our multisite replication setup by dedicating specifc RGW services for each tipe of request: Client Facing or Multisite replication . Part Three available
here.
Links to the rest of the blog series:
IBM Storage Ceph resources
Find out more about IBM Storage Ceph
#Highlights
#Highlights-home