ILE COBOL now supports Format 2 of the SORT statement to sort a table in release 7.3. This support is provided in the following two PTF's (and their supersedes):
- Compiler PTF SI59006 for product 5770WDS
- Runtime PTF SI59845 for product 5770SS1
This new support allows you to specify a data item defined with an OCCURS clause as the subject of the SORT statement, as compared to format 1 of the SORT statement which requires a file name.
Format 2: Table SORT statement
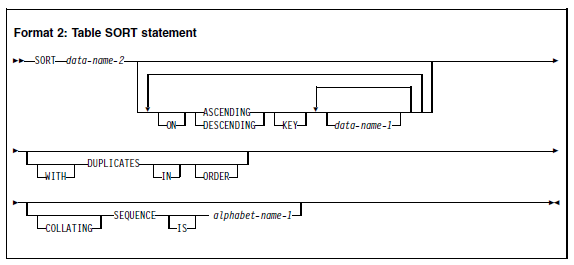
Format 2 SORT statements can appear anywhere in the PROCEDURE DIVISION.
data-name-2
Specifies a table data-name that is subject to the following rules:
- data-name-2 must have an OCCURS clause in the data description entry.
- data-name-2 can be qualified.
- data-name-2 can be subscripted. The rightmost or only subscript of the
table must be omitted or replaced with the word ALL.
The number of occurrences of table elements that are referenced by
data-name-2 is determined by the rules in the OCCURS clause. The sorted
table elements are placed in the same table that is referenced by
data-name-2.
ASCENDING KEY and DESCENDING KEY phrases (format 2)
This phrase specifies that table elements are to be processed in ascending or
descending sequence, based on the specified phrase and sort keys.
data-name-1
Specifies a KEY data name that is subject to the following rules:
- The data item that is identified by a key data-name must be the same as,
or subordinate to, the data item that is referenced by data-name-2.
- KEY data items can be qualified.
- KEY data items can belong to any of the following data categories:
- Alphabetic, alphanumeric, alphanumeric-edited
- Numeric
- Numeric-edited
- Internal floating-point or external floating-point
- National, national-edited, DBCS, or DBCS-edited
- KEY data items cannot be:
- Variably located
- Group items that contain variable-occurrence data item
- USAGE POINTER, USAGE PROCEDURE-POINTER
- Subscripted
- If the data item that is identified by a KEY data-name is subordinate to
data-name-2, the following rules apply:
- The data item cannot be described with an OCCURS clause.
- The data item cannot be subordinate to an entry that is also
subordinate to data-name-2 and that contains an OCCURS clause.
The KEY phrase can be omitted only if the description of the table that is
referenced by data-name-2 contains a KEY phrase.
The words ASCENDING and DESCENDING are transitive across all occurrences of
data-name-1 until another word ASCENDING or DESCENDING is encountered.
The data items that are referenced by data-name-1 are key data items, and these
data items determine the order in which the sorted table elements are stored. The
order of significance of the keys is the order in which data items are specified in
the SORT statement, without regard to the association with ASCENDING or
DESCENDING phrases.
The SORT statement sorts the table that is referenced by data-name-2 and presents
the sorted table in data-name-2. The sorting order is determined by either the
ASCENDING and DESCENDING phrases (if specified), or by the KEY phrase that
is associated with data-name-2.
The direction of the sorting operation depends on the specification of the
ASCENDING or DESCENDING keywords:
- When ASCENDING is specified, the sequence is from the lowest key value to
the highest one.
- When DESCENDING is specified, the sequence is from the highest key value to
the lowest one.
- If the KEY data item is DBCS, DBCS-edited, national, or national-editedthe
sequence of the KEY values is based on the binary values of the national characters.
- If the KEY data item is internal floating-point, the sequence of key values is in
the numeric order.
- When the COLLATING SEQUENCE phrase is not specified, the EBCDIC
sequence is used for key data items of alphabetic, alphanumeric,
alphanumeric-edited, external floating-point, and numeric-edited categories. For
all the other key data items, the comparisons are performed according to the
rules for comparison of operands in a relation condition.
- When the COLLATING SEQUENCE phrase is specified, the indicated collating
sequence is used for key data items of alphabetic, alphanumeric,
alphanumeric-edited, external floating-point, and numeric-edited categories. For
all the other key data items, the comparisons are performed according to the
rules for comparison of operands in a relation condition.
To determine the relative order in which table elements are stored, the contents of
corresponding key data items are compared according to the rules for comparison
of operands in a relation condition. The sorting starts with the most significant key
data item with the following rules:
- If the contents of the corresponding key data items are not equal and the key is
associated with the ASCENDING phrase, the table element that contains the key
data item with the lower value has the lower occurrence number.
- If the contents of the corresponding key data items are not equal and the key is
associated with the DESCENDING phrase, the table element that contains the
key data item with the higher value has the lower occurrence number.
- If the contents of the corresponding key data items are equal, the determination
is based on the contents of the next most significant key data item.
If the KEY phrase is not specified, the sequence is determined by the KEY phrase
in the data description entry of the table that is referenced by data-name-2.
If the KEY phrase is specified, it overrides any KEY phrase specified in the data
description entry of the table that is referenced by data-name-2.
If data-name-1 is omitted, the data item that is referenced by data-name-2 is the key
data item.
DUPLICATES phrase (format 2)
When both of the following conditions are met, the contents of table elements are
in the relative order that is the same as the order before sorting operation:
- The DUPLICATES phrase is specified.
- The contents of all the key data items that are associated with one table element
are equal to the contents of corresponding key data items that are associated
with one or more other table elements.
If the DUPLICATES phrase is not specified and the second condition exists, the
relative order of the contents of these table elements is undefined.
COLLATING SEQUENCE phrase (formats 1 and 2)
This phrase specifies the collating sequence to be used in alphanumeric
comparisons for the KEY data items in this sorting operation.
The COLLATING SEQUENCE phrase has no effect for keys that are not alphabetic
or alphanumeric.
alphabet-name-1
Must be specified in the alphabet-name clause of the SPECIAL-NAMES
paragraph. Any one of the alphabet-name clause options may be specified. See
"SPECIAL-NAMES Paragraph" for a list of alphabet-name clause
options and their meanings.
When the COLLATING SEQUENCE phrase is omitted, the PROGRAM
COLLATING SEQUENCE clause (if specified) in the OBJECT-COMPUTER
paragraph specifies the collating sequence to be used.
When both the COLLATING SEQUENCE phrase and the PROGRAM COLLATING
SEQUENCE clause are omitted, the EBCDIC collating sequence is used.
PhilsCafe