By:Arun Mani
Developer - OpenStack for POWER
In case of a failure in a scale environment, it can be really difficult to diagnose and fix problems. Sometimes an even bigger problem can be identifying that you have a problem in the first place.
This is a general troubleshooting guide for the most common issues faced with the PowerVC management server and doesn't cover troubleshooting any specific issues related to different components. This information is designed for system programmers and administrators, but can be used by anyone responsible for diagnosing problems related to the PowerVC management server.
To troubleshoot problems that are specific to a component, please refer to the troubleshooting section in the PowerVC Knowledge Center, which has more details on the problems and the workarounds available.
Suggested troubleshooting steps:
#1 Verify the PowerVC services status
#2 Validate your environment
#3 Check resource usage and availability and health
#4 Validate RMC service and Health state
#5 Analyze console messages
#1 Verify the PowerVC services status:
To make sure that all of the services in PowerVC are up and running, run /opt/ibm/powervc/bin/powervc-services status. If you need to check the service status of a specific PowerVC component, you can add that to the command. For example, you could run /opt/ibm/powervc/bin/powervc- services nova status. This will give the status of all the nova related services and help you figure out if the services are actually running or inactive (dead).
If you face any issues with service startup or configuration, try restarting the service that you think is having the problem or restart all PowerVC services by using the powervc-services command.
#2 Validate your environment:
This is one of the unique features of PowerVC. It enables you to validate the infrastructure after setting up PowerVC. Because there can be so many resources interplaying in a virtualization environment, verifying your environment plays a big role in problem solving.
The set of validations that are part of the validation tool covers the common configurations that are necessary to get optimal results and usage from the PowerVC server. The validations range from a simple ping test, to verifying shared storage pool configuration and storage connectivity.
You can run these validations by clicking the 'Verify Environment' button in the PowerVC interface on the home page. If you aren't able to access the user interface, you can use the 'powervc-validate' command instead.
#3 Check resource usage and availability and health:
PowerVC requires minimum hardware and software requirements to be installed and running. One of the most common issues that customers hit is the management server running out of disk space. Root cause analysis have shown that the problem is often one of these:
- Database configuration.
- Issues with services that start dumping messages in the log files, which leads to service becoming dead once disk size limit is reached.
- Huge data getting stored in the database on the management server that needs to be backed up frequently.
When configuring the PowerVC management server, it is important to ensure that it has enough resources. Even when your server meets the minimum requirements, its resources might soon be exhausted once you start registering resources and scaling up the environment. Detailed information about the hardware and software requirements can be found in the PowerVC Knowledge Center
It is important to monitor the management server's resource usage and take actions to control memory usage. These actions include cleaning up the old log files and backing up, then removing other files as necessary. Controlling disk storage usage avoids any critical downtime and ensures that the environment is effectively managed and the managed resources continues to run without any issues.
If you hit issues like this and want to know where exactly problem could be, you can leverage the 'Verify Environment' feature, which will scan the environment for any problems and reports it back to the user for better way of handling it.
Health of Managed resources:
In the PowerVC user interface, you can quickly determine when any of your managed resources have a problem. Resource health defines the state of the system at a point in time, and you might have to take certain actions if its not OK. See Health status is not OK in the PowerVC Knowledge Center for help if the health status changes.
#4 Validate RMC service and Health state:
One of the common issues after setting up the management server and registering resources is that the health state is not 'OK' for any of the hosts or its associated virtual machines.
One of the common problems related to this could be that the state of RMC subsystem running on HMC/LPAR's is not responding or goes down on its own, due to some problem with the platform manager or VIOS. This service is responsible for establishing a management domain between the HMC and LPARs that has the HMC as its Management Control Point (MCP). In case if you notice a change in health state caused by an issue with RMC service, follow the steps for fixing this here: Resource Monitoring and Control(RMC)
#5 Analyze console messages:
Prior to debugging logs for any issues that you notice in your environment, review the console messages for errors. You can view all the messages that were generated in your PowerVC environment on the 'Messages' tab in the home page of PowerVC user interface. To easily differentiate between an error and an informational message, review the 'Type' column of the message.
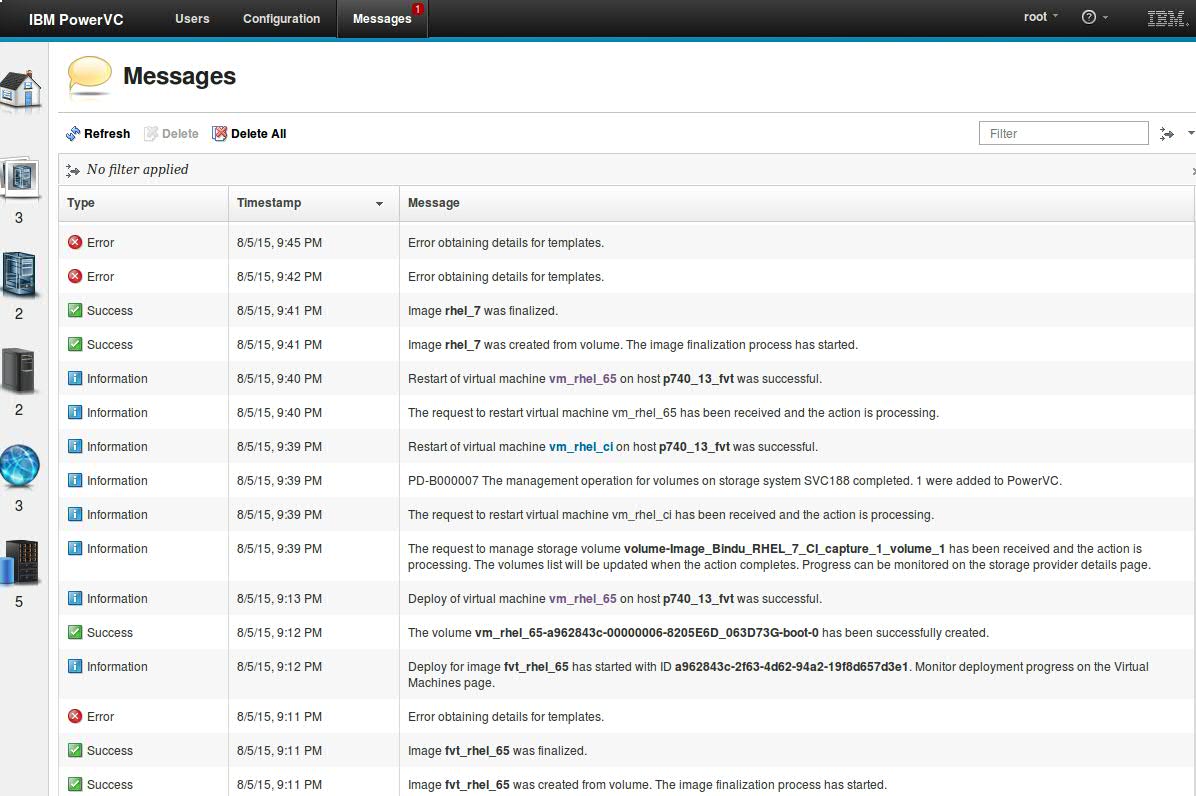
To enable faster debugging of these messages, you can filter these messaged based on a keyword search. Once you understand where the problem is by looking at the console message, you can view the specific log file related to the problem.
Other helpful topics:
The PowerVC Knowledge Center has other helpful troubleshooting topics including these:
If these suggestions don't resolve the problem, please refer to the PowerVC Knowledge Center or contact the support team for assistance. Questions or comments? Respond to this post or send your comment via LinkedIn, Twitter, or Facebook!