Originally posted by: Juan Yang
 Workload placement within the multicluster feature in IBM Spectrum Symphony Advanced Edition allows you to submit workload to under-utilized clusters within the multicluster. Workload placement minimizes application runtime, so that workload can be distributed across two or more clusters, thereby, rebalancing the work. You configure rules for both a global (cluster-level) workload placement policy, and also application-level workload placement policies (called workload bins), which you can then assign to different applications. IBM Spectrum Symphony then determines the eligible clusters, based on these rules, and distributes workload on them to maximize efficiency.
Workload placement within the multicluster feature in IBM Spectrum Symphony Advanced Edition allows you to submit workload to under-utilized clusters within the multicluster. Workload placement minimizes application runtime, so that workload can be distributed across two or more clusters, thereby, rebalancing the work. You configure rules for both a global (cluster-level) workload placement policy, and also application-level workload placement policies (called workload bins), which you can then assign to different applications. IBM Spectrum Symphony then determines the eligible clusters, based on these rules, and distributes workload on them to maximize efficiency.
 This blog guides you through configuring both global and application workload placement policies using the IBM Spectrum Symphony multicluster cluster management console and CLI. Ensure you have the appropriate permissions before completing these tasks. For more information about permissions for managing workload placement, see the IBM Knowledge Center (https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSZUMP_7.2.0/sym_kc/sym_kc_managing_multicluster.html).
This blog guides you through configuring both global and application workload placement policies using the IBM Spectrum Symphony multicluster cluster management console and CLI. Ensure you have the appropriate permissions before completing these tasks. For more information about permissions for managing workload placement, see the IBM Knowledge Center (https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSZUMP_7.2.0/sym_kc/sym_kc_managing_multicluster.html).
The tasks within this blog work through a scenario with two clusters: Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122; and one application: symping7.2.
Part 1: Configuring the global workload placement policy
Step 1: Enable the multicluster proxy on each lone cluster
On each lone cluster that you want to use multicluster features (including workload placement), you enable a multicluster proxy on it. The proxy is a program that discovers hosts in the cluster and triggers actions to manage them. There is one multicluster proxy per cluster. Once you enable this multicluster proxy, the lone cluster can then join the federation cluster as a member cluster (as described in step 2), and then take advantage of multicluster features. To enable the multicluster proxy on a lone cluster:
- On a management host in the lone cluster, log on to the multicluster management console as a cluster administrator:
https://mg_host_name:8443/Platform
- From the Dashboard, select .
- Click SMCP to see the Service Profile (SMCP) page.
- Specify values for the following multicluster profile (SMCP) environment variables for each cluster type:
- SMC_KD_MASTER_LIST
Click and replace @SMC_KD_MASTER_LIST@, with the host name or IP address of your IBM Spectrum Symphony multicluster master cluster. In the example below, the IP address is 9.111.254.125.
- SMC_KD_PORT
Click and replace @SMC_KD_PORT@, with the VEMKD port number on the multicluster master cluster. In the example, the port is 10033.
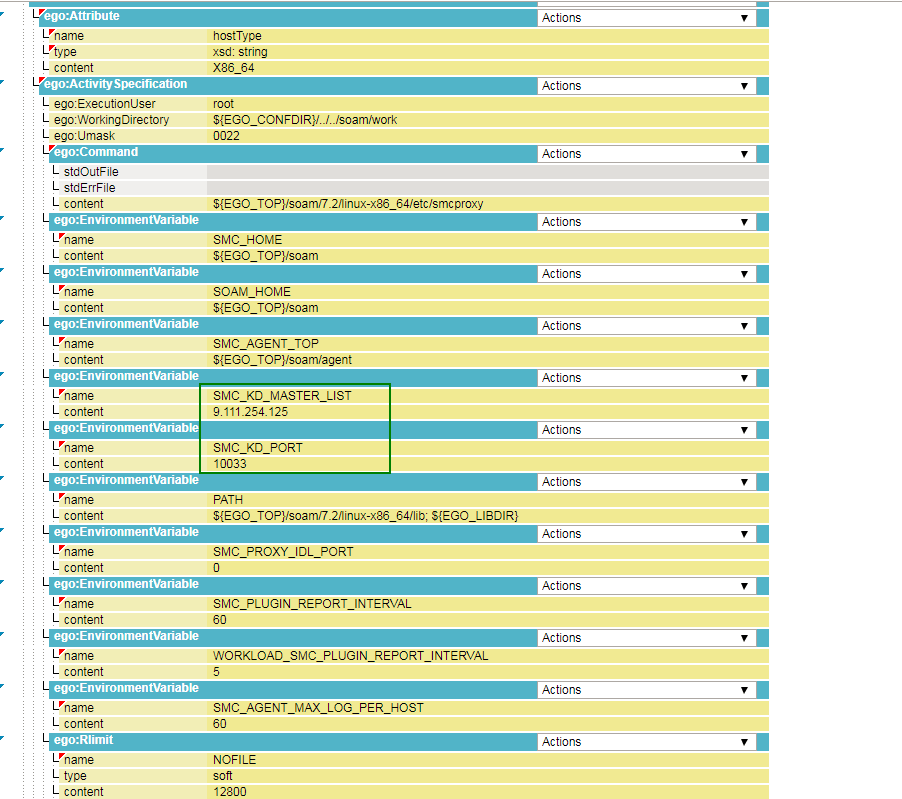
- Click Save and confirm your changes and close the Service Profile (SMCP) page.
- Start the multicluster proxy (SMCP) service: from the Services Profile page, choose Start from the Actions list and confirm your changes.
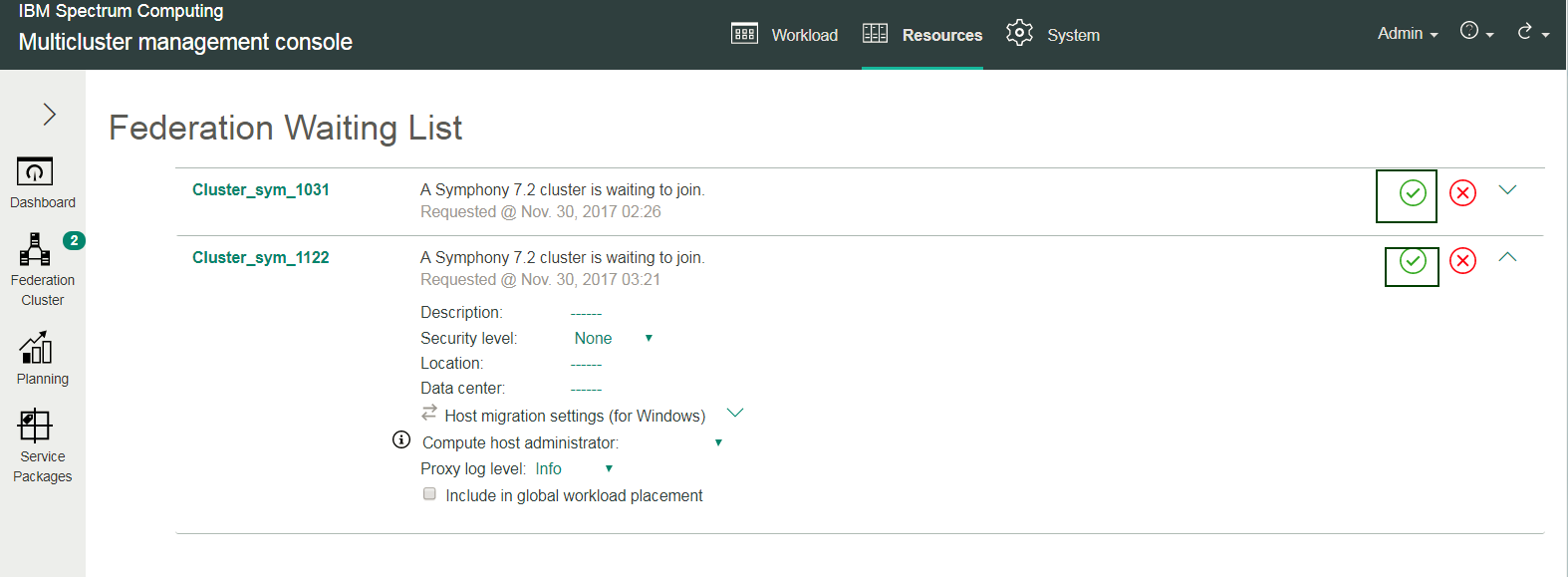
Step 2: Accept requests to join the federation cluster
The Federation Waiting List page lists the lone clusters that have requested to join the federation cluster. Before a cluster can participate in IBM Spectrum Symphony multicluster features (including workload placement), an administrator must accept a cluster's request to join the federation cluster:
- Click .
- Click the green check mark next to the cluster on the federation waiting list to accept the cluster's request to join the federation cluster, and then click Accept to confirm your action.
For example, here, two lone clusters, Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122, are waiting to be included in the federation cluster:
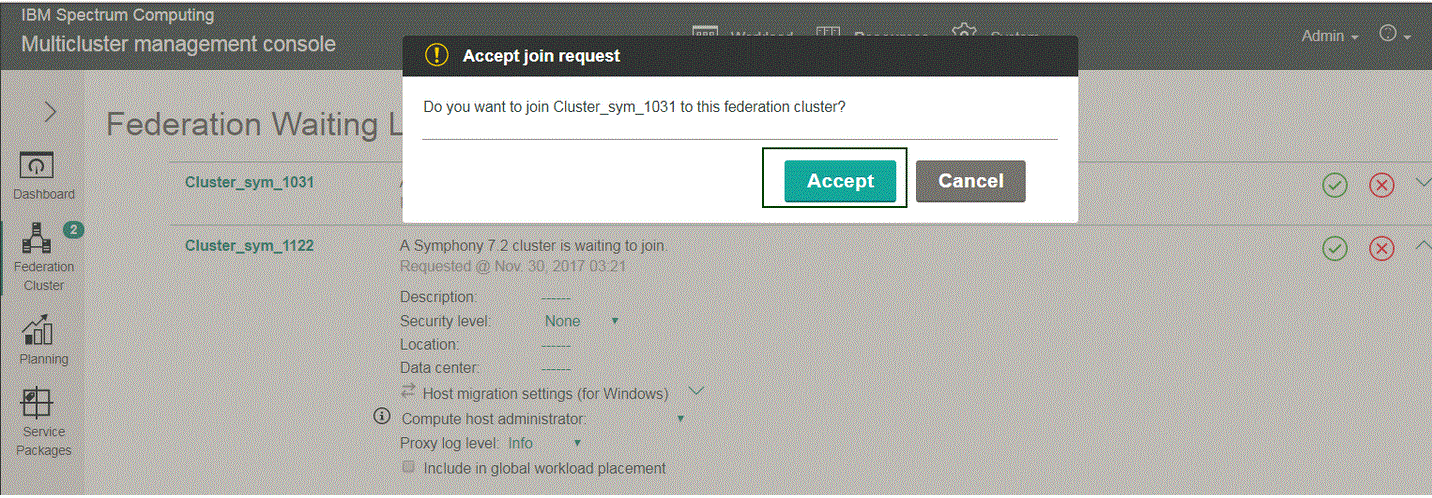
Upon clicking Accept, lone clusters Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122 become member clusters to the federation cluster.
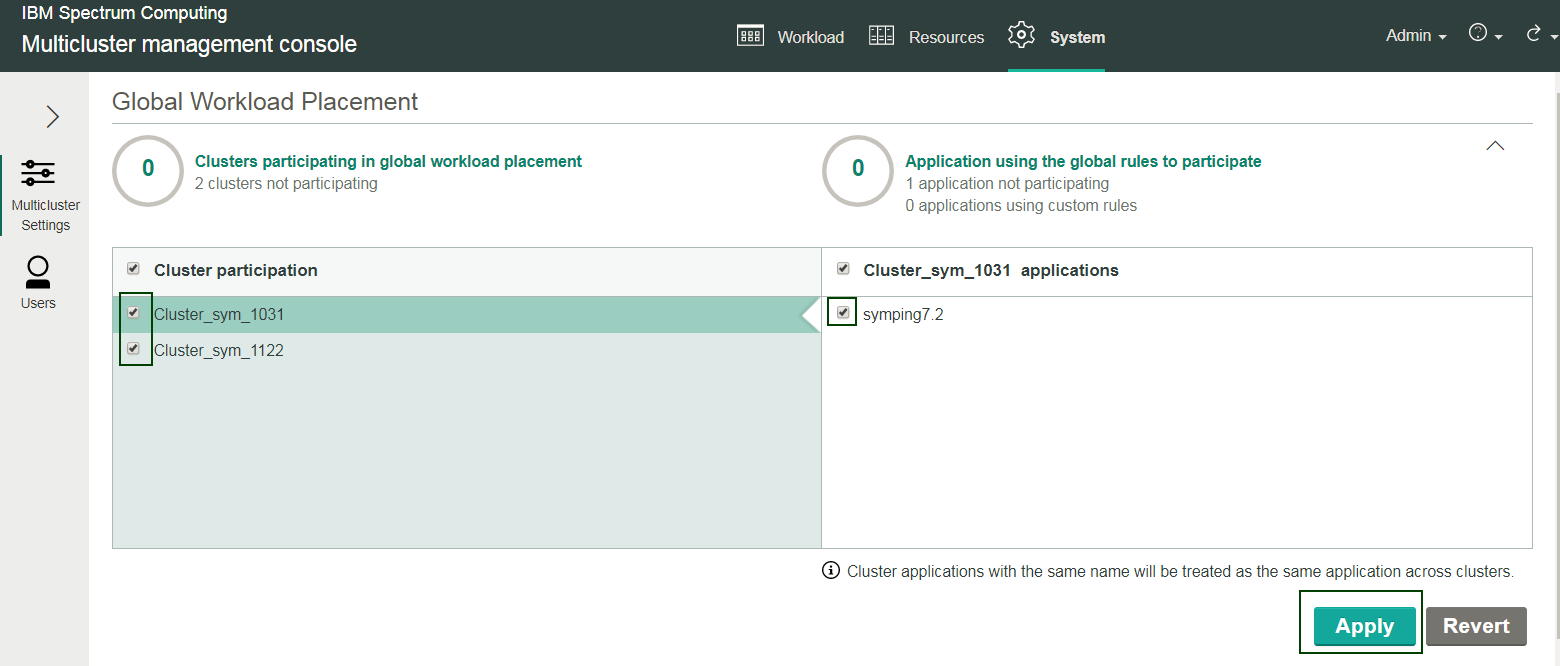
Step 3: Select clusters and applications to participate in workload placement
The member clusters that you allowed to join the federation cluster (that is, Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122), can now participate in workload placement. You must select these member clusters, and select at least one application, to use workload placement:
- Click .
Note that initially, you start with no clusters or applications participating in workload placement (as indicated with 0 of both Clusters participating in global workload placement and Application using the global rules to participate). There are two clusters waiting (as indicated by the 2 clusters not participating status), and one application waiting (as indicated by the 1 application not participating status).
-
Check clusters Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122 to allow the two waiting clusters to participate in workload placement.
- Check application symping7.2 to indicate you want this application to participate in workload placement for the two clusters.
- Click Apply.
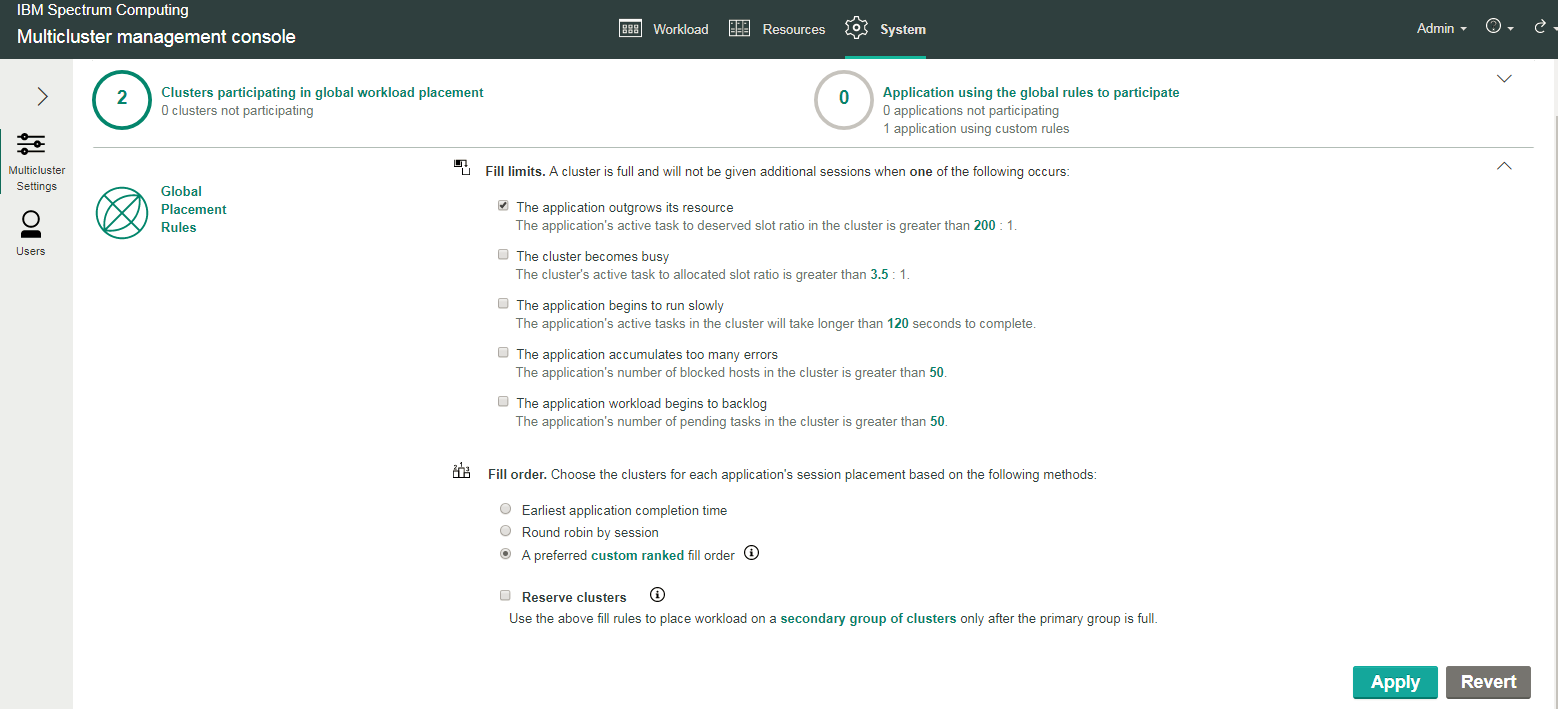
Step 4: Define global placement rules
With global workload placement, you use the built-in policy for the global rules for workload placement, and modify it for your needs. You can determine criteria to fill clusters with workload, and selecting a ranking method for filling the clusters:
- Click .
- In the Fill limits section, select the criteria that governs how workload should be placed (filled) in all clusters participating in workload placement. Note that you can select multiple options; the system will combine these options with AND logic.
- In the Fill order section, select a ranking method for filling the clusters:
- Earliest application completion time
Select this option if you want to always fill the clusters based on the cluster with the earliest completion time for the application.
- Round robin by session
Select this option if you want to always fill the clusters based on each application taking turns to fill the cluster.
- A preferred custom ranked fill order
Select this option if you want to always fill the clusters based on the available cluster closest to the beginning of a list of ranked clusters.
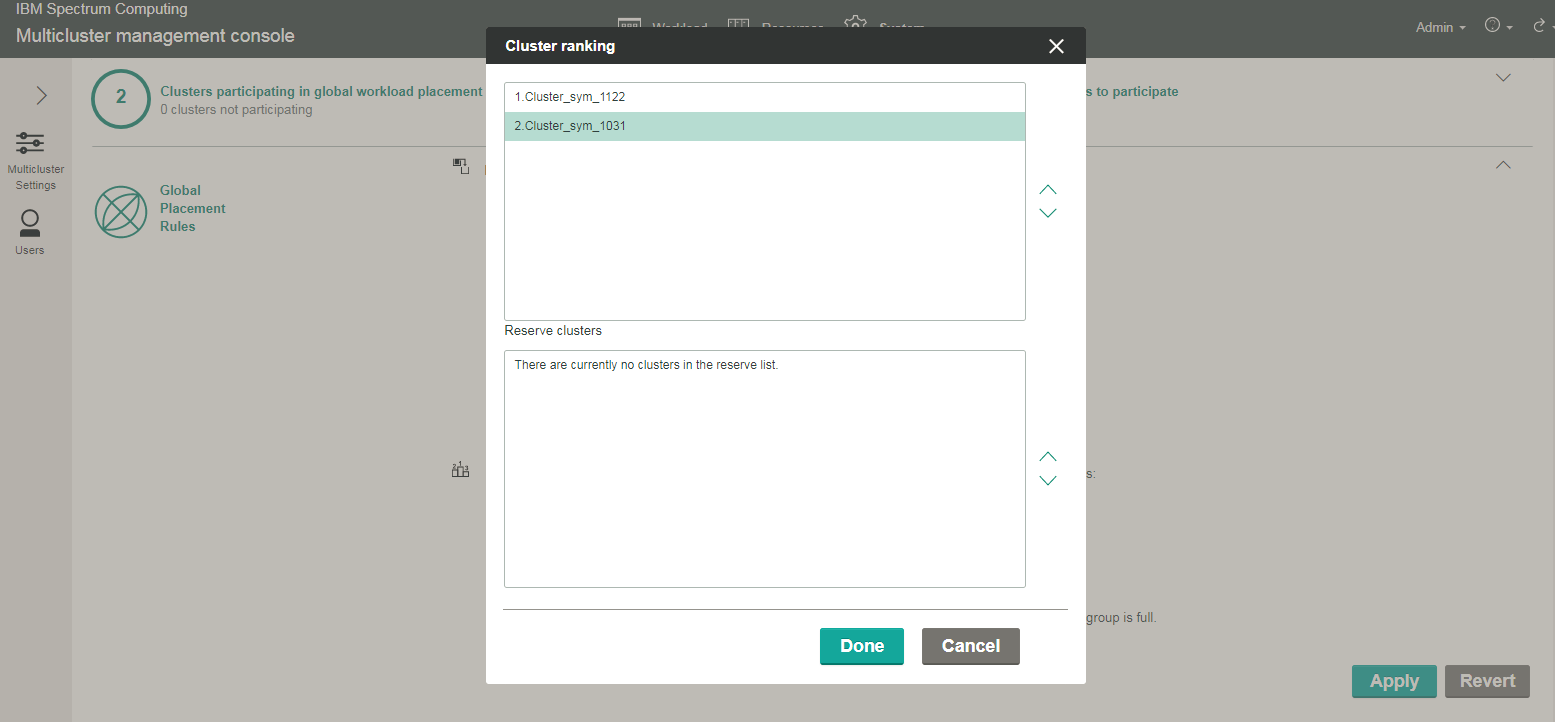
Click custom ranked to see a list of clusters to rank:
- Select and drag the cluster to move it up or down the list, so that the cluster first on your list is ranked as your preferred cluster. The cluster you move to the end of the list is your least preferred cluster. For example, in the following screenshot, Cluster_sym_1122 will be filled first because it is at the top of the list; Cluster_sym_1031 will be filled last.
- Click Done to save the custom ranking.
You can hover over the "i" icon next to A preferred custom ranked fill order to see the list of ranked clusters.
When clusters are filled with workload and you require more resources, you can use reserve clusters to accommodate the workload overflow. The reserved clusters are a secondary group of clusters after the primary group is filled with workload. Select Reserve cluster if you want to select clusters from your primary list of clusters to be in a secondary list of clusters used for the workload overflow.
Step 5: Check the status of clusters
You can use the CLI to verify the status of the member clusters by running the smcadmin cluster list command:
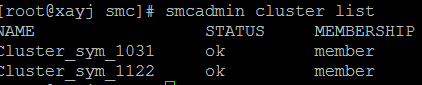
The status for both member clusters Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122 are OK and ready for workload placement.
Step 6: Enable member clusters to use workload placement
Now that you have set up your global workload placement policy, and before you can submit workload to the clusters, you must enable the SMC_GLOBAL_PLACEMENT environment variable on each member cluster. This allows the cluster to participate in workload placement. On both Cluster_sym_1033 and Cluster_sym_1122, run this command:
export SMC_GLOBAL_PLACEMENT=enabled
Step 7: Submit workload on each member cluster
To validate global workload placement on your member clusters, submit workload on each:
- On Cluster_sym_1122, run:
symping -m 600 -r 600000 &
When you see the message Session created. ID: session_ID@Cluster_sym_1031, this indicates that the cluster is used for workload placement and workload will be distributed on it:
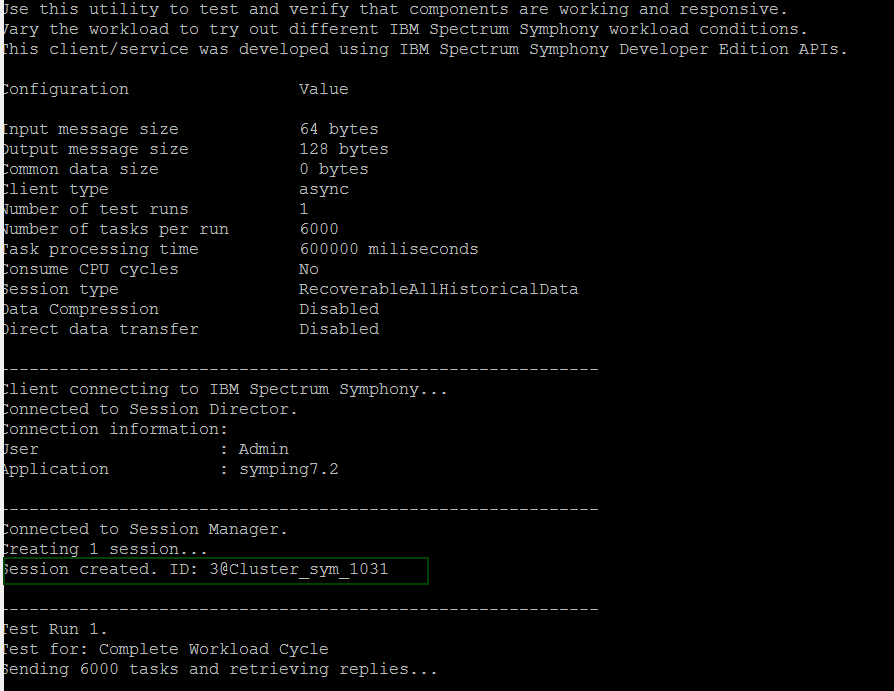
- On Cluster_sym_1031, run:
symping -m 6000 -r 600000 &
When you see the message Session created. ID: session_ID@Cluster_sym_1122, this indicates that the cluster is used for workload placement and workload will be distributed on it: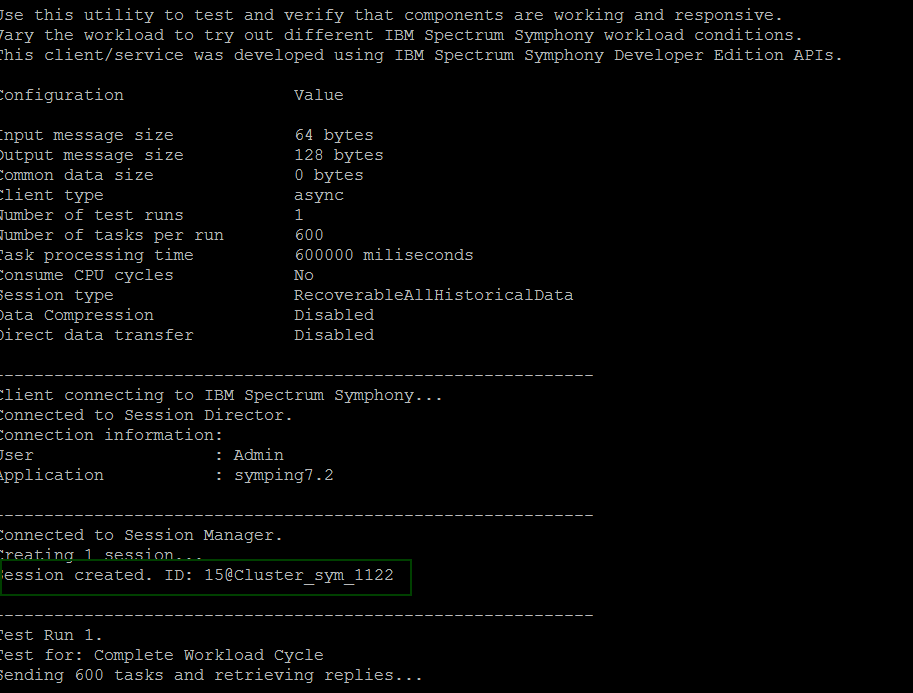
This completes your configuration for global workload placement. This next section discusses application workload placement, which has some similar tasks and the steps refer you to sections in "Part 1: Configuring the global workload placement policy".
Part 2: Configuring an application workload placement policy
The following steps for application workload placement continue after configuring a global workload placement policy. With application workload placement, you configure your own policies.
Step 1: Enable the multicluster proxy on each lone cluster
On each lone cluster that you want to use multicluster features (including workload placement), you enable a multicluster proxy on it.
You may have enabled the multicluster proxy on lone cluster Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122 in step 1 of "Part 1: Configuring a global workload placement policy". If so, skip to the next step. If you have not completed this step, follow the steps in step 1 of "Part 1: Configuring a global workload placement policy".
Step 2: Accept requests to join the federation cluster
The Federation Waiting List page lists the lone clusters that have requested to join the federation cluster. Before a cluster can participate in IBM Spectrum Symphony multicluster features (including workload placement), an administrator must accept a cluster's request to join the federation cluster.
You may have accepted lone cluster Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122 to join the federation cluster in step 2 of "Part 1: Configuring a global workload placement policy". If so, skip to the next step. If you have not completed this step, follow the steps in step 2 of "Part 1: Configuring a global workload placement policy".
Step 3: Show the applications selected to participate in workload placement
In step 3 of "Configuring a global workload placement policy", you selected the symping7.2 application to participate in workload placement. It is now listed under the Applications list on the Applications Settings page:
- Click .
- Expand the arrow within Application Settings.
- Under Applications, you can see the symping7.2 application. Select it to associate it with the workload placement policy:
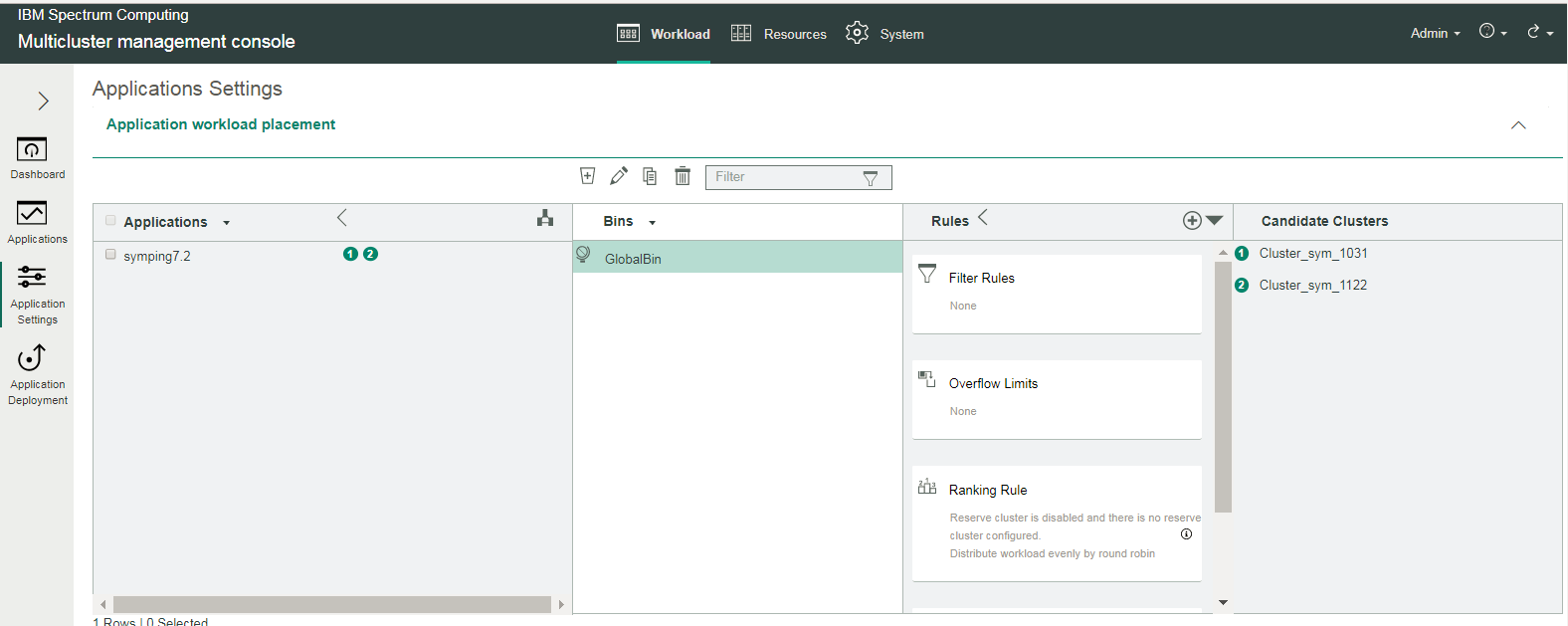
Step 4: Define your application workload placement policy (workload bin)
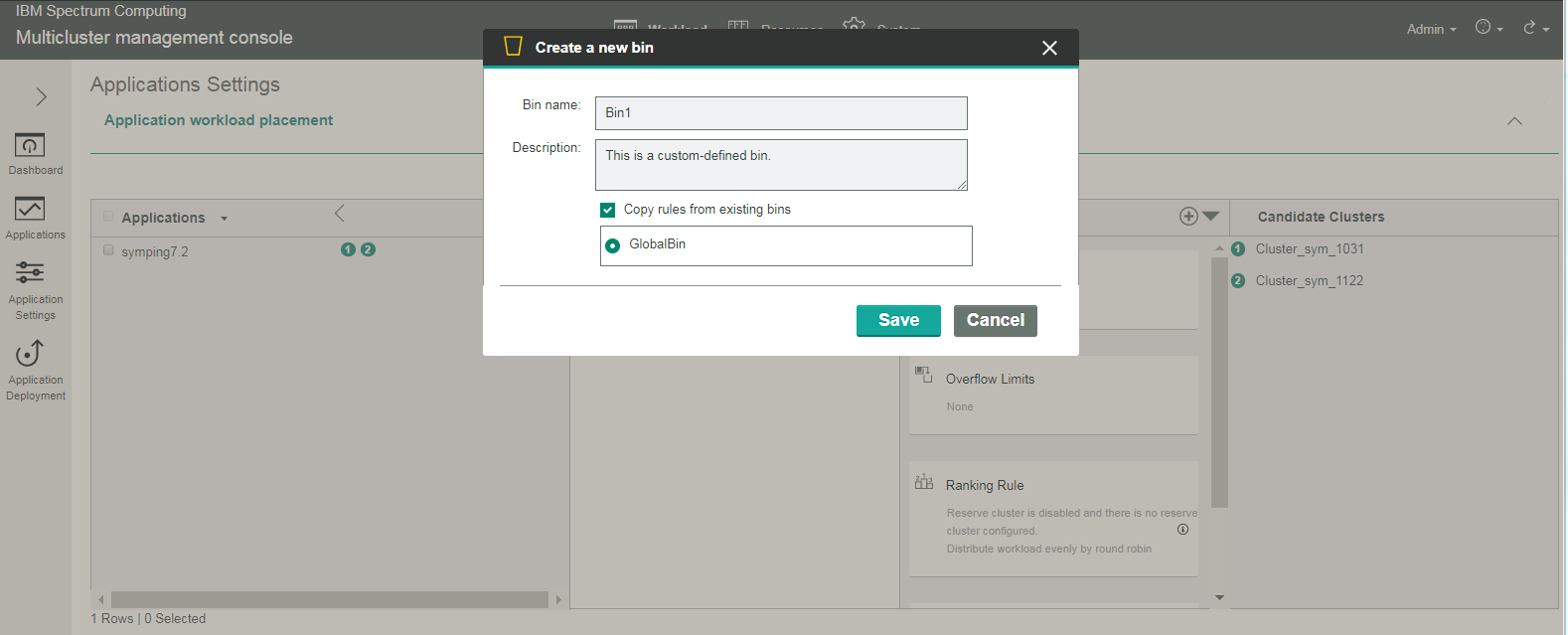
For application workload placement, unlike global workload placement, you define your own policies. These application workload placement policies are called workload bins, or simply bins. There is also a default a global bin, but in this example, you will create your own custom bin (called Bin1), and then associate the symping7.2 application with this bin.
To create a bin, clicking the add bin () icon from the menu list, which opens a create dialog. Provide a bin name (required) and description (optional), and click Save.
You can copy the rules from an existing bin. By default, the application workload placement policy will copy rules from the global workload placement policy, and apply it.
Step 5: Assign the new bin to an application
Highlight the bin name (here, it's, Bin1), and select the application name (symphony7.2) under Applications.
Application symping7.2 is then associated with the bin called Bin1:
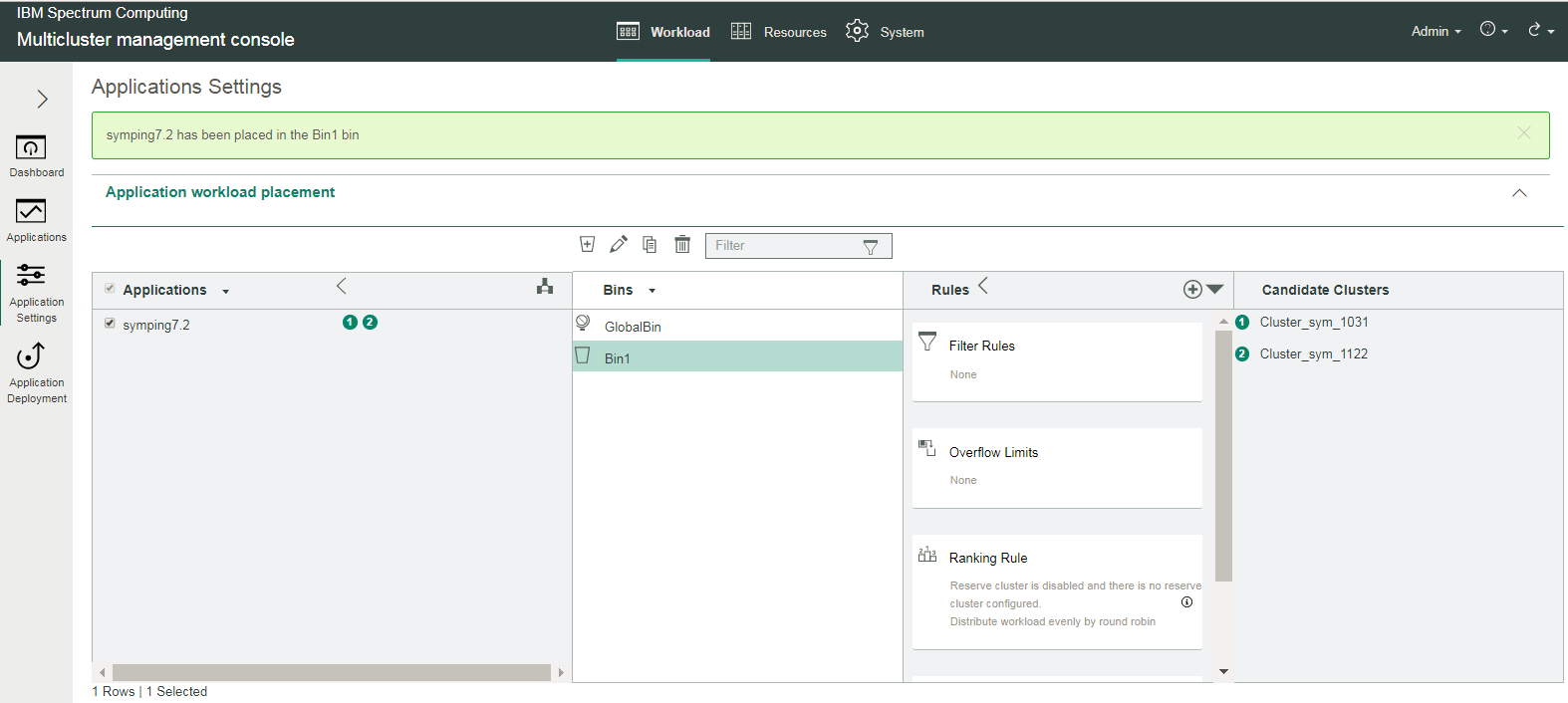
Step 6: Set static filter rules for the bin
Filter rules are static (that is, they do not, or rarely, change), such as the cluster name. These rules can be combined with one another, using AND and OR operators.
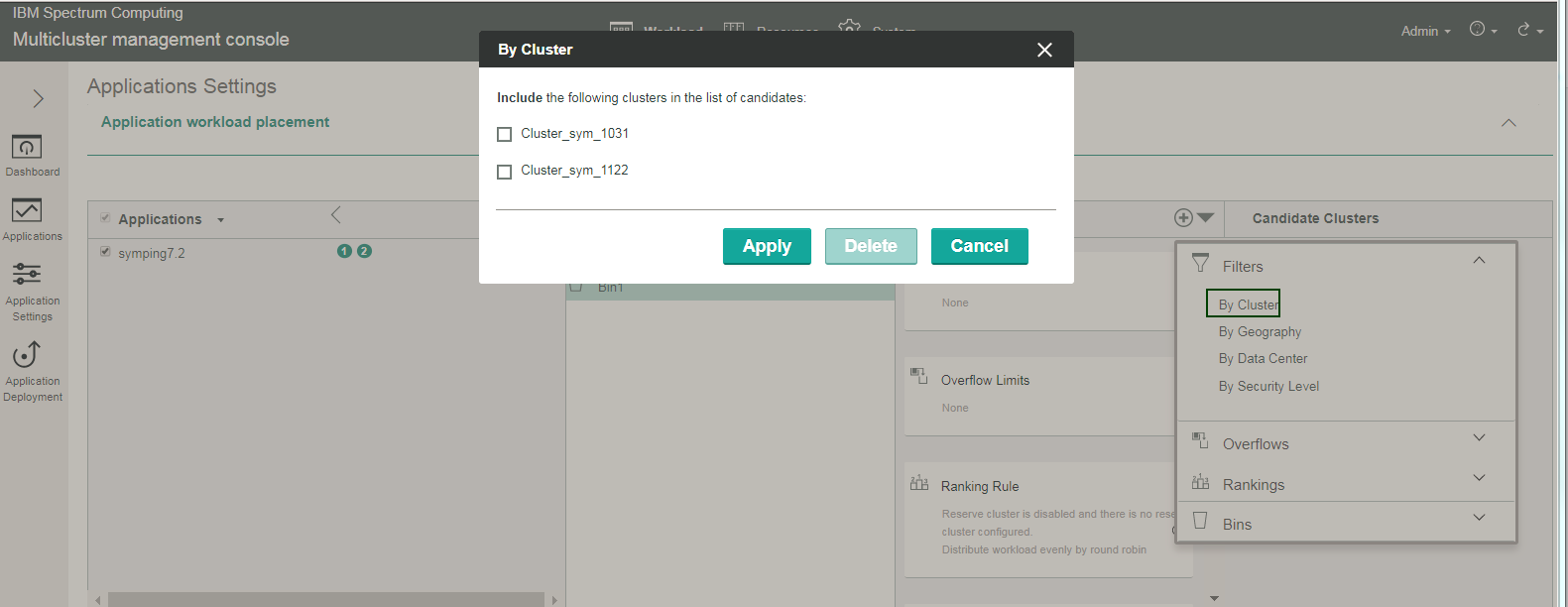
To set filter rules, under Bins, select the bin (Bin1), and within Rules, expand the arrow and select . Select the types of filter rules with which to work:
- By Cluster
To filter workload placement by specific clusters, select the clusters names, and click Apply. These cluster names are from your list of candidate clusters (under Candidate Clusters) for workload placement. Only these clusters will be used for workload placement for the application.
- By Data Center
To filter workload placement by specific data centers, select the data centers, and click Apply. Only clusters from these data centers will be used for workload placement or the application.
- By Security Level
To filter workload placement by cluster security level, select one of the security levels, and click Apply. Only the clusters with this security level will be used for workload placement for the application.
- By Geography
To filter workload placement by a specific cluster geographical range, select the country, state or province, and city combination, and click Apply. Only clusters within this geographical range will be used for workload placement for the application.
Here is an example of a filter rule by cluster; the clusters checked in the list will be used for workload placement:
Step 7: Set dynamic workload overflow limit rules for the bin
Workload overflow limit rules are based on metrics that are dynamic and can change often, such as the number of blocked hosts. These rules can be combined with one another, using AND and OR operators.
When clusters are filled with workload and you require more resources, you can use reserve clusters to accommodate the workload overflow. The reserved clusters are a secondary group of clusters after the primary group is filled with workload.
To set overflow limit rules, under Bins, select the bin (for example, Bin1), and within Rules, expand the arrow, and select Overflow Limits. You can set rules about workload overflow by configuring these overflow limit rules:
- Rate of active task to deserved slot
To limit workload placement by a defined active task to deserved slot ratio, specify the maximum number of active tasks per deserved slot for an application in the cluster, and click Apply. When the application's active task to deserved slot ratio in the cluster is greater than maximum_number_of_active_tasks to one, then workload overflows to a reserved cluster.
- Rate of task to slot limit
To limit workload placement by a defined active task to allocated slot ratio, specify the maximum number of active tasks per allocated slot for a cluster, and click Apply. When the cluster's active task to allocated slot ratio is greater than maximum_number_of_active_tasks to one, then workload overflows to a reserved cluster.
- Task completion time on active application
To limit workload placement by the total amount of time to complete an application's active task, select the maximum number of seconds that the application's active tasks in the cluster can take to complete before workload overflows, and Apply. When the cluster's active task complete by this duration, then workload overflows to a reserved cluster.
- Application blocked hosts
To limit workload placement by the number of blocked hosts in the cluster, specify the maximum number of blocked hosts before workload overflows, and click Apply. When this number of hosts are blocked in the cluster, then workload overflows to a reserved cluster.
- Number of pending tasks for active application
To limit workload placement based on the number of pending tasks for an application, specify the maximum number of pending tasks in the cluster before workload overflows, and click Apply. When this number of tasks are pending in the cluster, then workload overflows to a reserved cluster.
Step 8: Set ranking rules for the bin
IBM Spectrum Symphony uses ranking rules to determine the order to distribution clusters and fill them with workload. By default, the round robin ranking method is used.
To change the ranking rules, under Bins, select the bin (Bin1), and within Rules, expand the arrow, select Rankings, then select one of the following ranking rules to fill clusters:
When clusters are filled with workload and you require more resources, you can use reserve clusters to accommodate the workload overflow. The reserved clusters are a secondary group of clusters after the primary group is filled with workload. Select Reserve cluster if you want to select clusters from your primary list of clusters to be in a secondary list of clusters used for the workload overflow.
Step 9: Enable member clusters to use workload placement
Now that you have set up your application workload placement policy, Bin1, and before you can submit workload to the clusters, you must enable the SMC_GLOBAL_PLACEMENT environment variable on each member cluster.
This allows the cluster to participate in workload placement.
You may have enabled the multicluster proxy on lone cluster Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122 in step 6 of "Part 1: Configuring a global workload placement policy". If so, skip to the next step. If you have not completed this step, follow the steps in step 6 of "Part 1: Configuring a global workload placement policy".
Step 10: Submit workload on each member cluster
To validate application workload placement on your member clusters, submit workload on each:
On Cluster_sym_1031, run:
symping -m 600 -r 600000 &
On Cluster_sym_1122, run:
symping -m 600 -r 600000 &
Similar to step 7 of "Part 1: Configuring a global workload placement policy, when you see the message Session created. ID: session_ID@cluster_name, the cluster is used for workload placement and workload will be distributed on it.
Step 11: Check your application workload placement configuration by viewing the the candidate clusters list
Both member clusters (Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122) are now used and contain workload. Therefore, there are currently no candidate clusters free and available to receive workload, as illustrated under the Candidate Clusters section here:
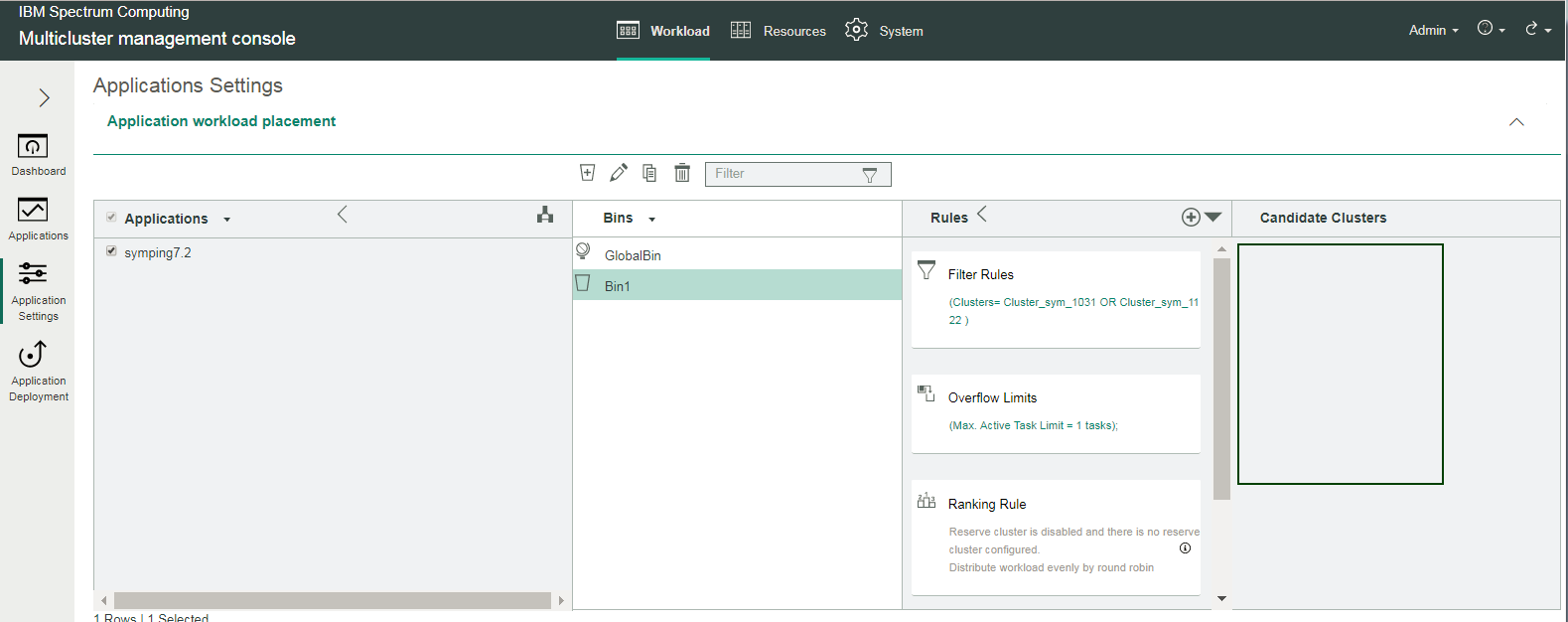
All done! This completes your configuration for application workload placement.
Final thoughts
This blog illustrated the benefits of workload placement within the IBM Spectrum Symphony multicluster feature. It used a simple scenario of configuring a global workload placement policy, and an application placement policy (Bin1) to best distribute workload across two clusters (Cluster_sym_1031 and Cluster_sym_1122) for application symping7.2.
If you'd like more information about the workload placement, for the IBM Spectrum Symphony multicluster feature, see IBM Knowledge Center:
https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSZUMP_7.2.0/multicluster_user/chap_smc_global_placement.html
Symphony then determines the eligible clusters, based on these rules, and distributes workload on them to maximize efficiency.
#SpectrumComputingGroup