Microsoft Entra ID, previously known as Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), is a multi-tenant cloud-based directory and identity management service from Microsoft. Microsoft Entra ID extends on-premises Active Directory into the cloud.
Using Microsoft Entra ID with IBM® App Connect
You can use App Connect to perform actions on the following objects:
- Administrative units
- Devices
- Domains
- Groups
- Organizations
- Users
Building a flow in App Connect with Microsoft Entra ID
You can now use IBM App Connect to build flows that integrate with Microsoft Entra ID and other applications.
The connector is displayed as “Microsoft Entra ID” on the IBM App Connect User Interface (UI).
You can opt to log in by using the basic, or OAuth 2.0 password authentication mode. The required information to connect App Connect to your Microsoft Entra ID account differs based on the authentication mode.
For App Connect deployments in containerized environments, the following properties are required for your Microsoft Entra ID account connection.
|
Required credentials
|
Description
|
|
Client ID
|
The unique identifier generated after the Microsoft Azure app registration gets mapped to the specific project requests.
Note: Only required for OAuth 2.0 password and basic authentication mode.
|
|
Client secret
|
The application client secret for a project-specific unique application client ID.
Note: Only required for OAuth 2.0 password and basic authentication mode.
|
|
Access token
|
The access token generated from the application client ID and client secret.
Note: Only required for basic authentication mode.
|
|
Refresh token
|
The refresh token generated from the application client ID and client secret.
Note: Only required for basic authentication mode.
|
|
Username
|
The username to log in to your Microsoft Azure Active Directory account.
Note: Only required for OAuth 2.0 password authentication mode.
|
|
Password
|
The password for the specified username.
Note: Only required for OAuth 2.0 password authentication mode.
|
Now, let’s look at the Microsoft Entra ID use cases that are run in a containerized environment.
Scenario 1: Syncs Microsoft Active Directory computers to Microsoft Entra ID
Consider this scenario where you use App Connect that schedules an hourly synchronization scheduler-based flow between the Microsoft Active Directory (AD) and Entra ID devices in a containerized environment.
The flow creates or updates the device in Microsoft Entra ID whenever a new computer is created or updated in Microsoft AD, helping you keep your devices information in sync.
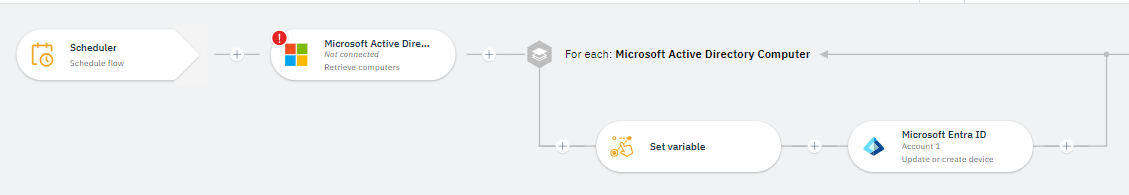
For this scenario:
1. You run a scheduler-based flow that retrieves computers from Microsoft Active Directory (AD) through a batch process.
2. The Microsoft AD retrieve computers operation fetches the computer details based on the base-distinguished name.
For example: 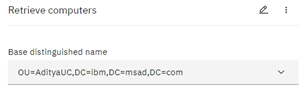
3. A Set variable node is added to a ‘For each’ loop to map the retrieved computer with a common name string.
For each Microsoft AD computer is mapped with a common name string.
For example:
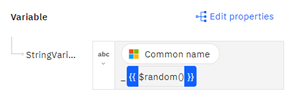
This setting generates random data with the common name, making it a unique entry for Entra ID.
4. The Microsoft Entra ID update or create device operation either updates or creates the device details based on the device registration ID mapped to the retrieved computer common name.
For example:
If the device is not found, the device details are created, or for an existing device, the details are updated accordingly in Microsoft Entra ID.
Scenario 2: Syncs Microsoft Active Directory users to Microsoft Entra ID