Enter the following values:
· AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID – From AWS access configuration
· AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY -> From AWS access configuration
· Default Region Name -> Region name where your cluster is running
· Default output format -> Text
The next step is to update the Kubernetes config file. Execute the following command.
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region yourclusterregion --name yourclustername
You should get a response similar to the following.

Verify the access to your cluster is working with the following command.
You should get something similar to the following.

Installing cert-manager in your Kubernetes cluster
Use the following steps to install cert-manager (IBM Documentation reference here)
1. Open a command line window
2. Execute the following command
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.12.10/cert-manager.yaml
3. Verify the installation
kubectl get pods --namespace cert-manager
You should get something similar to the following picture.

4. Patch the deployment
From a GitBash command window, execute the following command to patch the cert-manager deployment
kubectl patch deployment \
cert-manager \
--namespace cert-manager \
--type='json' \
-p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/args", "value": [
"--v=2",
"--cluster-resource-namespace=$(POD_NAMESPACE)",
"--leader-election-namespace=kube-system",
"--enable-certificate-owner-ref"
]}]'
You should get the following response.

5. Go to next step install IBM AppConnect Operator using Helm
Install IBM AppConnect Operator using Helm with the following steps.
1. Add the Helm Chart repository with the following command.
helm repo add ibm-helm https://raw.githubusercontent.com/IBM/charts/master/repo/ibm-helm
2. Create a namespace for the operator
Create a namespace for the operator. For example -> appconnectee
kubectl create namespace appconnectee
3. Set the context to the created namespace -> appconnectee
Set the current context to the created namespace executing the following command.
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=appconnectee
4. Create an image pull secret in the namespace where you want to deploy the Operator
The image pull secret is used to access the container images from the IBM Entitled Registry. You need to obtain the Entitlement Key from the IBM Container Software library - https://myibm.ibm.com/products-services/containerlibrary . Create a new entitlement key or copy an existing entitlement key to create the image pull secret in the following step.
Execute the following command to create the image pull secret
kubectl create secret docker-registry ibm-entitlement-key --docker-server="cp.icr.io" --docker-username=cp --docker-password="myEntitlementKey"
5. Install the operator
Execute the following command to install the operator. Note that we are using the namespace appconnectee in this command.
helm install ibm-appconnect ibm-helm/ibm-appconnect-operator -n appconnectee --set namespace="appconnectee" --set operator.installMode="AllNamespaces"
After the command has completed you should get the following output.

To verify the installation of the operator execute the following command.
You should get a response similar to the following picture.
Run the following command to verify the operator pod is running
You should get a response with a pod that starts with ibm-appconnect- and in running status

Create the NGINX Controller for external access to the cluster resources
We need to create an ingress controller to allow external access to the app connect resources. The appendix one has the awsnginxcontroller.yml file. Copy the provided text and create the awseksnginxcontroller.yml file. To create the ingress controller execute the following steps.
1. Create the namespace for the ingress controller with the following commands.
Kubectl create namespace ingress-nginx
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=ingress-nginx
2. Create the ingress controller executing the following command.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.3.0/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml -n ingress-nginx
After completing the execution of the command you should see something like the following picture.

3. Verify the ingress controller
We need to verify the ingress cotroller creation and the access to the external IP. It is important to mention that the assignment of the external IP or DNS takes a few minutes. Execute the following commands to verify your ingress controller
Kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx
You should get something similar to the following:

Take note of the External IP value of the ingress-nginx-controller service. Copy the External IP value and execute the following command.
Nslookup EXTERNAL-IP
You should get something similar to the following.

Next we need to verify if the external ip is accessible. We will use CURL for this. Execute the following CURL command (I am using GitBash on Windows for this).
curl -v External IP Address
You should get something similar to the following screen.

Take note of the IP Address is the response. We will use this address to provision the first App Connect resource (Dashboard). Another option to verify the external ip is accessible is to use a web browser with the external ip value. You should get the 404 Not Found Nginx html as a response.

If all is good you can proceed to the next step which is provisioning the first App Connect resource.
Creating the App Connect Dashboard
In this section we will create an App Connect Dashboard to deploy integrations in a runtime environment. Before creating the dashboard we need to verify we have the required storage class available.
Storage requirements
The App Connect Dashboard requires a ReadWriteMany storage class. To list your available storage classes execute the following command.
You should get the list of storage classes defined in your cluster.

Take note of the one that has as provisioner – efs.csi.aws.com. In this case is efs-sc. We will use this storage class when defining the dashboard resource.
Dashboard Resource
Before creating the dashboard.yml file you should go to the License Reference for IBM App Connect Operator 13 page in the following link https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/app-connect/13.0?topic=resources-licensing-reference-app-connect-operator . In this scenario we are using the AppConnectEnterpriseNonProductionFREE license with value -> L-KPRV-AUG9NC (See the yml file below).
1. Create the following yml file – appconnectdashboard1.yml
apiVersion: appconnect.ibm.com/v1beta1
kind: Dashboard
metadata:
name: appconnecteedashboard1
labels:
namespace: appconnectee
spec:
license:
accept: true
license: L-KPRV-AUG9NC
use: AppConnectEnterpriseNonProductionFREE
pod:
containers:
content-server:
resources:
limits:
memory: 1024Mi
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 100Mi
control-ui:
resources:
limits:
memory: 1024Mi
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 500Mi
authentication:
integrationKeycloak:
enabled: false
authorization:
integrationKeycloak:
enabled: false
ingress:
domain: XX.XX.XX.XX.nip.io
api:
enabled: true
storage:
size: 5Gi
type: persistent-claim
class: efs-sc
displayMode: IntegrationServers
replicas: 1
version: '13.0'
It is important to mention the following:
· Name of the dashboard is appconnecteedashboard1
· License.use is the AppConnectEnterpriseNonProductionFREE
· License.value L-KPRV-AUG9NC
· Authentication and authorization are disabled (false)
· The ingress domain is build with the external ip value you got from nslookup or/and the curl command + nip.io -> XX.XX.XX.XX.nip.io
· Storage.class: efs-sc
2. Create the dashboard executing the following command
kubectl apply -f appconnectdashboard1.yml -n appconnectee
3. Verify the creation of the dashboard.
Wait for a minute and execute the following commands to obtain the dashboard and service details.
kubectl get dashboard -n appconnectee
You should get something similar to the following screen.

Verify the status of the dashboard is Ready. Now execute the following command.
kubectl get svc -n appconnectee
You should get something similar to the following screen.

Note the name of the service. It is built with the dashboard name + -dash. In this example is appconnecteedashboard1-dash. Take note of this name. We will use it to create the ingress resource to the service that will allow to access the dashboard UI.
Copy the following text to create the awsingress.yml file.
4. Create the ingress resource for the dashboard
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTPS
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffer-size: 16k
creationTimestamp: "2025-03-14T13:00:16Z"
generation: 4
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: control-ui
app.kubernetes.io/instance: appconnecteedashboard1
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: ibm-appconnect
app.kubernetes.io/name: appconnecteedashboard1
appconnect.ibm.com/kind: Dashboard
release: appconnecteedashboard1
name: appconnecteedashboard1-ui
namespace: appconnectee
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: appconnecteedashboard1-ui-appconnectee.XX.XX.XX.XX.nip.io
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: appconnecteedashboard1-dash
port:
number: 8300
path: /
pathType: Prefix
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- ip: XX.XX.XX.XX
Update the value of the ip address on the spec.host and status.loadBalancer.ingress.ip elements. Note the value of the host is built with dashboardname + -ui- + namespace + .externalip + .nip.io
Create the ingress resource executing the following command.
kubectl apply -f awsingress1.yml -n appconnectee
5. Access the dashboard
Open your web browser and go the following URL:
https://dashboardname + -ui- + namespace + .externalip + .nip.io . In this case is https://appconnecteedashboard1-ui-appconnectee.XX.XX.XX.XX.nip.io where XX.XX.XX.XX is your external ip address obtained with curl when the nginx-controller was created.
Accept the security warning messages and proceed to the URL. You should see the App Connect EE dashboard UI.

Deploy an integration to test the App Connect installation
In this section we will deploy a simple REST Service integration built with the App Connect toolkit. The REST service receives 2 numbers as input parameters and returns the sum of the numbers. We will deploy the integration and test it with Postman.
1. Deploy the integration
On the Dashboard click on Deploy integrations and on the Deploy integrations page click on Quickstart integration and then click Next

On the next page upload your bar file. In this case is the MathAPIproject.generated.bar file. The bar file is available on the following github repository jeanpaultabja/appconnect: Assets for App Connect installation tutorial
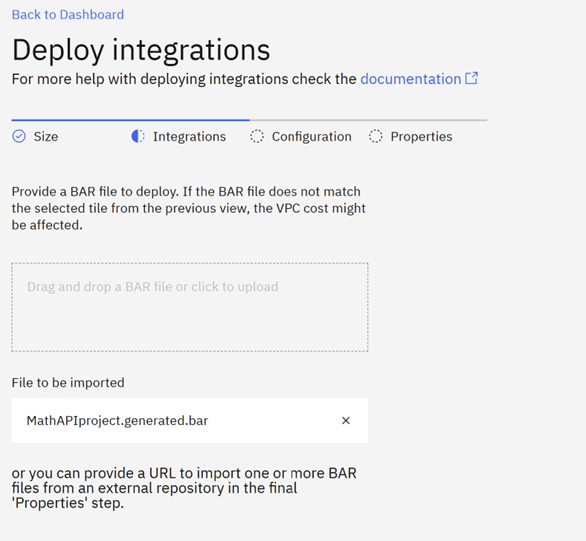
Click Next and on the configurations page Click Next again. In the next page enter the name of the integration, the channel and the license information and the click on Create.

Wait for a couple of minutes and you should have an integration server on the servers tab with Ready status.

You should have your integration on the integrations tab

Click on the integration to see the details of the REST Service API – MathAPI. Clid the Get /getSum operation for complete details.

2. Create the ingress resource for the deployed integration artifact
We need to create the ingress resource for the deployed integration artifact. Copy the following text and create the mathapiingress.yml file
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: mathapi-service-ingress
namespace: appconnectee
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
spec:
rules:
- host: is-01-quickstart-is-appconnectee.XX.XX.XX.XX.nip.io
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
backend:
service:
name: is-01-quickstart-is
port:
number: 7800
Note the name of the host is built using integrationname-namespace.externalip.nip.io . In this example integration name is is-01-quickstart-is . Execute the following command to create the ingress resource for the integration.
kubectl apply -f mathapiingress.yml -n appconnectee
The next step is to test the integration with Postman
3. Test the integration
Open PostMan and configure the test with the following parameters.
- Operation: GET
- URL: http://is-01-quickstart-is-appconnectee.XX.XX.XX.XX .nip.io/mathapi/v1/getSum (where XX.XX.XX.XX is your external ip)
- Input variables:
The following screen shows the Postman configuration for the test
 If the test succeeded with the expected result and a 200 return code the installation and configuration of App Connect has been successfully completed.
If the test succeeded with the expected result and a 200 return code the installation and configuration of App Connect has been successfully completed.