Setup Amazon Cognito and IBM MQ to provide JWKS Signing Guide
By Harry Pearce
Guide Disclaimer and Platform Notes
This guide is not official IBM documentation and is not supported by IBM. It has been created based on individual experience and is intended for educational or personal use only. Use at your own discretion, and consult official IBM and AWS documentation for production-grade implementations.
Guide accurate as of July 2025.
This guide was developed using the following platforms:
- Console: x86_64 GNU/Linux
- Browser: Firefox 141.0 (aarch64)
- MQ: IBM MQ 9.4.3.0 running in containers (Podman)
If you're using different platforms, some steps may vary slightly and should be adjusted accordingly.
This guide demonstrates how to integrate Amazon AWS Cognito with IBM MQ using JWT-based authentication. It walks through creating a Cognito user pool and app client, registering and authenticating a user to obtain an access token, configuring an IBM MQ Queue Manager to trust Cognito’s JWKS for token validation, and finally building a simple JMS application that retrieves a Cognito access token and sends messages to the queue. The goal is to establish a secure, token-driven authentication flow between your application and MQ.
- Create and Configure a User Pool in AWS Cognito
- Register and Authenticate a User
- Install MQ in a Container
- Configure MQ Queue Manager to accept authentication via JWKS
- Test with a JMS Application
Note: This tutorial uses the eu-west-2 (London) region. If you prefer to use a different region, you can switch it using the region selector in the top menu bar on any AWS page. All links in this guide will direct you to the London region, so please ensure the correct region is selected before proceeding.
1. Create and Configure a User Pool in AWS Cognito
This section outlines how to set up a new user pool in AWS Cognito with the desired configuration and create an app client for authentication purposes.
-
To Create a new Amazon Cognito User pool:
- From the AWS Console Home Page search for and select Cognito.
- Open the top-left hamburger menu and click 'User pools'.
- Click either of the 'Create user pool' buttons.
-
In the Create User Pool form configure the following:
- Application Type: Select 'Single-page application (SPA)'.
- Client application name: Enter a name such as
MQ-Cognito-JWKS-Guide. (Note: this name identifies the client app resource, not the user pool itself, which is named by AWS).
- Sign-in method: Choose Username.
- Required attributes for sign-up: Add email.
- Return URL: Leave this field blank.
- Click the 'Create user directory' button at the bottom-right to finalise and create the user pool.
Example: A completed form for creating a new Amazon Cognito user pool and app client.
Upon pressing 'Create user directory', a green confirmation popup will appear, indicating that the app client and user pool has been successfully created:
Your application "MQ-Cognito-JWKS-Guide" and user pool "User pool - ylwozo" have been created successfully! Follow the instruction to continue the setup.
-
Apply the necessary client app authentication flow setting:
-
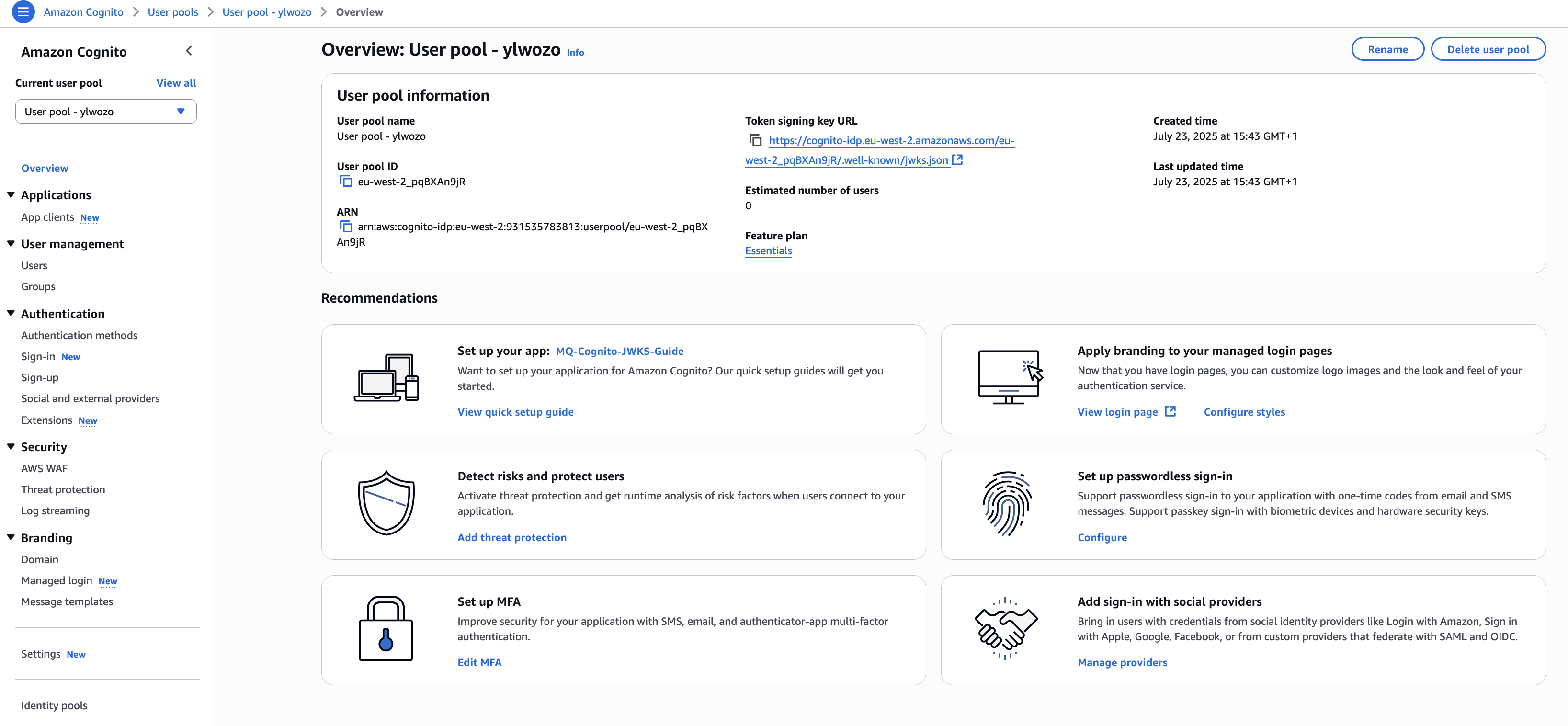
Go to the User pools Overview page:
- From the AWS Console Home Page search for and select Cognito.
- Open the top-left hamburger menu and click 'User pools'.
- Click on your user pool name e.g. 'User pool - ylwozo.
- This will take you to the User pool Overview page.
Example: the unmodified User Pool Overview page for 'User pool - ylwozo'.
-
Edit the App Client Settings:
- In the left-hand menu, under Applications select 'App clients'.
- Click on the App Client you created earlier e.g. 'MQ-Cognito-JWKS-Guide'.
- In the 'App client information' panel, click the 'edit' button.
Example: The unmodified 'App Client Overview' with edit button highlighted for 'MQ-Cognito-JWKS-Guide'.
-
Enable the Required Authentication Flow:
- On the 'Edit app client information page', enable the checkbox for: 'Sign in with username and password: ALLOW_USER_PASSWORD_AUTH'
- Click 'Save Changes' in the bottom right corner of the form.
Example: App Client Settings with the 'ALLOW_USER_PASSWORD_AUTH' enabled.
-
Save the App Client ID
On the 'Client App Overview' make a note of the 'Client ID'
For example:
Client ID: 45r7hahlvntu2mrrgkc0di8of3
This ID will be required later when authenticating users and configuring your application.
Example: Find Client ID
Register and Authenticate a User
This section explains how to add a user to the Cognito user pool and authenticate them to obtain tokens—Access, ID, and Refresh—which are used for secure communication with downstream services.
Register a User in AWS Cognito
-
Create a New User in the Cognito User Pool:
- From the AWS Console Home Page search for and select Cognito.
- Open the top-left hamburger menu and click User pools.
- Click on your user pool name, e.g. 'User pool - ylwozo.
- In the left-hand menu select 'Users' under 'User Management'.
- Click either of the Create user buttons.
-
Fill out the Create User Form:
- Username: app
- Email: Use an email address you currently have access to.
- Password: P@ssw0rd
- Click 'Create user' at the bottom-right of the form.
Example: Completed 'Create user' form. Note: A made up email has been added to this example.
Authenticate the user using the REST API
Using curl commands, you will need to log in to the Cognito user pool, respond to the password challenge by setting a new password, and retrieve the user's personal Access Token.
Optional: If you add your cognito credentials as environment variables you can copy most of the Structure examples directly to your terminal.
export COGNITO_CLIENT_ID=45r7hahlvntu2mrrgkc0di8of3
export COGNITO_USERNAME=app
export COGNITO_PASSWORD=P@ssw0rd
export COGNITO_REGION=eu-west-2
Use cURL to Log in to the Cognito User Pool as app:
Structure:
curl -X POST --data '{
"AuthParameters": {
"USERNAME": "'"$COGNITO_USERNAME"'",
"PASSWORD": "'"$COGNITO_PASSWORD"'"
},
"AuthFlow": "USER_PASSWORD_AUTH",
"ClientId": "'"$COGNITO_CLIENT_ID"'"
}' \
-H 'X-Amz-Target: AWSCognitoIdentityProviderService.InitiateAuth' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-amz-json-1.1' \
https://cognito-idp.$COGNITO_REGION.amazonaws.com/
Example (based on this tutorial):
- Client ID: 45r7hahlvntu2mrrgkc0di8of3
- Username: app
- Password: P@ssw0rd
- Region: eu-west-2
curl -X POST --data '{
"AuthParameters": {
"USERNAME": "app",
"PASSWORD": "P@ssw0rd"
},
"AuthFlow": "USER_PASSWORD_AUTH",
"ClientId": "45r7hahlvntu2mrrgkc0di8of3"
}' \
-H 'X-Amz-Target: AWSCognitoIdentityProviderService.InitiateAuth' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-amz-json-1.1' \
https://cognito-idp.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/
Running the previous command will trigger a challenge requiring the user to set a new password. Here’s an example response (simplified for readability):
{
"ChallengeName": "NEW_PASSWORD_REQUIRED",
"ChallengeParameters": {
"USER_ID_FOR_SRP":"app",
"requiredAttributes":"[]",
"userAttributes":"{\"email\":\"<your-email-here>\"}"
},
"Session":"<session-token>"
}
Note: The <session-token> is required for the next step in the authentication flow. The email shown will match the one used during user creation.
Optional: Set new password with environment variable.
export COGNITO_PASSWORD=P@ssw0rd1
Structure:
Note: Make sure to replace <session-token> with your session token retrived from the step above.
curl -X POST --data '{
"ChallengeName": "NEW_PASSWORD_REQUIRED",
"ClientId": "'"$COGNITO_CLIENT_ID"'",
"ChallengeResponses": {
"NEW_PASSWORD": "'"$COGNITO_PASSWORD"'",
"USERNAME": "'"$COGNITO_USERNAME"'"
},
"Session": "<your-session-token>"
}' \
-H 'X-Amz-Target: AWSCognitoIdentityProviderService.RespondToAuthChallenge' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-amz-json-1.1' \
https://cognito-idp.$COGNITO_REGION.amazonaws.com/
Example (based on this tutorial):
- Client ID: 45r7hahlvntu2mrrgkc0di8of3
- Username: app
- New Password: P@ssw0rd1
- AWS Region Endpoint: eu-west-2
Note: Session code has been omitted and replaced with <session-token> due to length of message of around 800 characters.
curl -X POST --data '{
"ChallengeName": "NEW_PASSWORD_REQUIRED",
"ClientId":"45r7hahlvntu2mrrgkc0di8of3",
"ChallengeResponses": {
"NEW_PASSWORD": "P@ssw0rd1",
"USERNAME": "app"
},
"Session": "<session-token>"
}' \
-H 'X-Amz-Target: AWSCognitoIdentityProviderService.RespondToAuthChallenge' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-amz-json-1.1' \
https://cognito-idp.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/
- Response from successful challenge response:
Upon successfully responding to the challenge, you will receive a JSON response containing authentication data for the user. This data can be retrieved again later, so there's no need to store or process it immediately.
{
"AuthenticationResult": {
"AccessToken": "<access-token>",
"ExpiresIn": 3600,
"IdToken": "<id-token>",
"RefreshToken": "<refresh-token>"
"TokenType": "Bearer"
}
"ChallengeParameters": {}
}
If you wanted to get a new Access Token use the same CURL command you used to login to Cognito with the new password.
Structure:
curl -X POST --data '{
"AuthParameters": {
"USERNAME": "'"$COGNITO_USERNAME"'",
"PASSWORD": "'"$COGNITO_PASSWORD"'"
},
"AuthFlow": "USER_PASSWORD_AUTH",
"ClientId": "'"$COGNITO_CLIENT_ID"'"
}' \
-H 'X-Amz-Target: AWSCognitoIdentityProviderService.InitiateAuth' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-amz-json-1.1' \
https://cognito-idp.$COGNITO_REGION.amazonaws.com/
Example (based on this tutorial):
- Client ID: 45r7hahlvntu2mrrgkc0di8of3
- Username: app
- Password: P@ssw0rd1
- Region: eu-west-2
curl -X POST --data '{
"AuthParameters": {
"USERNAME": "app",
"PASSWORD": "P@ssw0rd1"
},
"AuthFlow": "USER_PASSWORD_AUTH",
"ClientId": "45r7hahlvntu2mrrgkc0di8of3"
}' \
-H 'X-Amz-Target: AWSCognitoIdentityProviderService.InitiateAuth' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-amz-json-1.1' \
https://cognito-idp.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/
3. Install MQ in a Container
For this tutorial I will be using MQ by through using a podman container. This example will be for using Linux, if you have a different operating system or want extra details look at the guide: Get an IBM MQ queue for development in a container tutorial on IBM Developer.
Install and confirm podman:
yum install podman
podman --version
If podman machine is not started use the following to start it:
Pull the MQ Container image:
podman pull icr.io/ibm-messaging/mq:latest
Create podman volume:
podman volume create qm1data
Run the container with sample values:
podman run --env LICENSE=accept --env MQ_QMGR_NAME=QM1 --volume qm1data:/mnt/mqm --publish 1414:1414 --publish 9443:9443 --detach --env MQ_APP_USER=app --env MQ_APP_PASSWORD=passw0rd --env MQ_ADMIN_USER=admin --env MQ_ADMIN_PASSWORD=passw0rd --name QM1 icr.io/ibm-messaging/mq:latest
Confirm the podman container is running:
4. Configure MQ Queue Manager to accept authentication via JWKS
Note: For this step you will require the Token signing key URL, You can find it in the User Pool Overview page.
When configuring your IBM MQ Queue Manager, you’ll need to define key settings in the qm.ini file. Three important components are:
-
SSL HTTPSKeyStore: This is the path to the keystore file that MQ will use for HTTPS communication. For this guide, the keystore file will be named:
-
JWKS Issuer Name:
This is the base URL of the Token signing key URL without the .well-known/jwks.json.
For this example:
https://cognito-idp.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/eu-west-2_pqBXAn9jR
-
JWKS End Point
This is the full URL of Token signing key URL without the .well-known/jwks.json.
For this example:
https://cognito-idp.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/eu-west-2_pqBXAn9jR/.well-known/jwks.json
-
JWKS UserClaim
This has to be the value username.
Example qm.ini configuration file with placeholders for JWKS IssuerName and Endpoint:
#*******************************************************************#
#* WARNING: Automatic configuration has been enabled for this *#
#* queue manager. Modifications in this file to anything other *#
#* than valid AutoConfig keys will be lost at the next Queue *#
#* Manager start. To disable automatic ini configuration, remove *#
#* the 'IniConfig' key from the AutoConfig stanza. *#
#*******************************************************************#
#
#*******************************************************************#
#* Module Name: qm.ini *#
#* Type : IBM MQ queue manager configuration file *#
# Function : Define the configuration of a single queue manager *#
#* *#
#*******************************************************************#
#* Notes : *#
#* 1) This file defines the configuration of the queue manager. *#
#* 2) The LogFilePages attribute is read-only and changes to it *#
#* will have no effect. *#
#* 3) The LogType attribute is read-only and changes to it will *#
#* have no effect. To change the log type of the queue manager *#
#* use the migmqlog command. *#
#* *#
#*******************************************************************#
ExitPath:
ExitsDefaultPath=/mnt/mqm/data/exits
ExitsDefaultPath64=/mnt/mqm/data/exits64
#* *#
#* *#
Log:
LogPrimaryFiles=3
LogSecondaryFiles=2
LogFilePages=4096
LogType=CIRCULAR
LogBufferPages=0
LogPath=/mnt/mqm/data/log/QM1/
LogWriteIntegrity=TripleWrite
Service:
Name=AuthorizationService
EntryPoints=14
SecurityPolicy=UserExternal
SSL:
HTTPSKeyStore=/var/mqm/qmgrs/QM1/ssl/mqdefcer.p12
Channels:
ChlauthEarlyAdopt=Yes
ChlauthIgnoreUserCase=No
TCP:
SndBuffSize=0
RcvBuffSize=0
RcvSndBuffSize=0
RcvRcvBuffSize=0
ClntSndBuffSize=0
ClntRcvBuffSize=0
SvrSndBuffSize=0
SvrRcvBuffSize=0
SecureCommsOnly=NO
AutoConfig:
MQSCConfig=/etc/mqm/
IniConfig=/etc/mqm/
Subpool:
ShortSubpoolName=QM10000
ServiceComponent:
Service=AuthorizationService
Name=Dev.HtpAuth.Service
Module=/opt/mqm/lib64/mqsimpleauth.so
ComponentDataSize=0
ServiceComponent:
Service=AuthorizationService
Name=MQSeries.UNIX.auth.services
Module=amqzfu
ComponentDataSize=0
JWKS:
IssuerName=<issuer-name>
Endpoint=<endpoint>
UserClaim=username
Copy qm.ini into the queue manager:
podman cp qm.ini QM1:/var/mqm/qmgrs/QM1
Retrieve Cognito's RootCA Certificate and signing URL.
This section explains how to download the JWKs from the Cognito endpoint, which are used to verify JWT signatures.
-
Go to the User pools Overview page:
-
From the AWS Console Home Page search for and select Cognito.
-
Open the top-left hamburger menu and click 'User pools'.
-
Click on your user pool name e.g. 'User pool - ylwozo.
-
This will take you to the User pool Overview page.
-
Follow the link to the Token signing key URL:
-
Go to the view certifcate page:
- Click the padlock icon.
- Click “Connection Secure” button.
- Click “More Information".
- Click “View Certificate” (in security tab).
- Select the “Amazon Root CA 1” certificate tab .
- Click download PEM(cert) to install the certificate.
-
Copy Amazon Root CA into the MQ Queue Manager:
Note: Ensure that the region specified in the Amazon Cognito .pem file matches your AWS region.
podman cp cognito-idp-eu-west-2-amazonaws-com.pem QM1:/var/mqm/qmgrs/QM1/ssl/
Configure the MQ Queue Manager to Trust Cognito
This section explains how to configure IBM MQ to trust Amazon Cognito by importing Cognito’s public key into the MQ trust store and enabling JWT-based authentication.
-
Access the IBM MQ Container Shell as the mqm User:
-
Create a PKCS12 key store named mqdefcer.p12:
opt/mqm/bin/runmqakm -keydb -create -db /var/mqm/qmgrs/QM1/ssl/mqdefcer.p12 -pw password -type pkcs12 -stash
-
Set Permissions on the Keystore Files:
chmod 777 /var/mqm/qmgrs/QM1/ssl/mqdefcer.*
-
Import the Cognito public certificate:
opt/mqm/bin/runmqakm -cert -add -db /var/mqm/qmgrs/QM1/ssl/mqdefcer.p12 -pw password -label cognitoPublicLabel -file /var/mqm/qmgrs/QM1/ssl/cognito-idp-eu-west-2-amazonaws-com.pem
-
Apply the changes by refreshing the queue manager's security:
echo "REFRESH SECURITY" | runmqsc QM1
-
Check the MQ error log for confirmation:
cat /var/mqm/qmgrs/QM1/errors/AMQERR01.LOG
You should see a message similar to:
07/24/25 18:03:55 - Process(1517.19) User(mqm) Program(amqzmur0)
Host(339d001f50dd) Installation(Installation1)
VRMF(9.4.3.0) QMgr(QM1)
Time(2025-07-24T18:03:55.528Z)
CommentInsert1(https://cognito-idp.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/eu-west-2_pqBXAn9jR)
AMQ5791I: Token authentication configuration loaded successfully for JWKS
issuer https://cognito-idp.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/eu-west-2_pqBXAn9jR from its
endpoint.
EXPLANATION:
Token authentication configuration has just been loaded successfully; this is
either the first time since the queue manager was started, or after the
previous token authentication configuration was revoked, or after previously
seeing an error.
ACTION:
None.
----- amqkjwta.c : 833 --------------------------------------------------------
Test with a JMS Application
This section walks through setting up a JMS client that connects to MQ using a Cognito-issued access token to verify secure messaging.
Prerequisite: to install java, javac and curl. On Red Hat Linux (RHEL) you can use the following commands:
yum install java
yum install java-devel
yum install curl
# Verify Java and javac installation
java -version
javac -version
curl --version
If you refer to the appendix, you'll find a complete script that installs all required dependencies and writes the necessary contents to the appropriate files. However, if you prefer a more detailed understanding or wish to perform the setup manually, please continue following the step-by-step instructions in this guide.
After install refer back to Running the application to learn how to run this java program.
Set-up directories and download dependencies:
Use these instructions to create the relevant directories for the application and to install all the required java packages.
mkdir MQClient
cd MQClient
curl -o com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/ibm/mq/com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client/9.4.2.0/com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar
curl -o jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/jakarta/jms/jakarta.jms-api/3.1.0/jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar
curl -o json-20250107.jar https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/json/json/20250107/json-20250107.jar
mkdir app
Create env.json configuration file:
Next, create the env.json file and make it match the following structure.
{
"MQ_CONFIG": {
"QMGR": "QM1",
"QUEUE_NAME": "DEV.QUEUE.1",
"CHANNEL": "DEV.APP.SVRCONN",
"PORT": "1414"
},
"COGNITO_CONFIG":{
"USERNAME": "app",
"PASSWORD": "P@ssw0rd1",
"CLIENT_ID": "",
"REGION" : "eu-west-2"
}
}
Note: CLIENT_ID must be your AWS Cognito ClientID and region must match that Cognito instance.
Create the Java Jakarta MQ App with Cognito JWKS-based-Authentication:
Inside the app create the mq.java and add the following java code.
package app;
import jakarta.jms.Destination;
import jakarta.jms.JMSConsumer;
import jakarta.jms.JMSProducer;
import jakarta.jms.JMSContext;
import jakarta.jms.JMSException;
import jakarta.jms.TextMessage;
import com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.jms.JmsConnectionFactory;
import com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.jms.JmsFactoryFactory;
import com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.wmq.WMQConstants;
import com.ibm.mq.constants.MQConstants;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest.BodyPublishers;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class mq {
// MQ Queue Manager Configuration.
private static String queueManager = "";
private static String queueName = "";
private static String channel = "";
private static int port = 0;
// Cognito JWKS Configuration.
private static String username = "";
private static String password = "";
private static String clientId = "";
private static String region = "";
/*
Purpose: This Java application demonstrates how to send and receive messages to/from an IBM MQ queue using
AWS Cognito for JWKS-based authentication.
Dependencies:
- Jakarta Messaging API (JMS) for MQ interaction.
- IBM MQ Java client libraries.
- AWS SDK for Java (specifically, HttpClient for Cognito token retrieval).
Configuration:
Environment variables for MQ connection details (queue manager, queue name, channel, port) and Cognito configuration details
(username, password, client ID, region) are loaded from the `env.json` file.
Flow:
- The application loads environment variables from env.json.
- Retrives an access token from AWS Cognito using the provided credentials and the HTTP package.
- Connects to the MQ queue and sends/receives messages specified by the arguments.
- After successful message exchange, it prints a success message and exits.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("\nJava Jakarta App to send message to MQ with AWS Cognito providing JWKS Authentication.\n");
// Load environment variables from env.json.
getEnvVars();
// Obtain access token from Cognito.
String accessToken = getCognitoAccessToken();
System.out.println("\nConnecting to MQ...");
if (args.length > 0) {
// Connect to MQ and use the command line arguments to send custom messages.
connectAndTestMQ(accessToken, args);
} else {
// Use default message if no arguments are provided
System.out.println("No arg messages found, using default test message.");
String[] msgs = {"Hello from MQ using AWS Cognito JWKS Token Authtentication!"};
// Connect to MQ using the defualt message.
connectAndTestMQ(accessToken, msgs);
}
System.out.println("\nSuccessfully completed MQ Cognito JWKS validation test.");
// Expected end of execution.
System.exit(0);
}
// connectAndTestMQ, establishes a connection to an MQ queue using provided credentials and sends/receives messages.
private static void connectAndTestMQ(String accessToken, String[] msgs){
JMSContext context = null;
Destination destination = null;
JMSProducer producer = null;
JMSConsumer consumer = null;
try {
System.out.println("Creating connection factory.");
JmsFactoryFactory ff = JmsFactoryFactory.getInstance(WMQConstants.JAKARTA_WMQ_PROVIDER);
JmsConnectionFactory cf = ff.createConnectionFactory();
// Set MQ connection properties.
cf.setIntProperty(WMQConstants.WMQ_CONNECTION_MODE, WMQConstants.WMQ_CM_CLIENT);
cf.setIntProperty(WMQConstants.WMQ_PORT, port);
cf.setStringProperty(WMQConstants.WMQ_CHANNEL, channel);
cf.setStringProperty(WMQConstants.WMQ_QUEUE_MANAGER, queueManager);
// Use the Cognito access token for authentication.
cf.setStringProperty(WMQConstants.PASSWORD, accessToken);
context = cf.createContext();
destination = context.createQueue("queue:///" + queueName);
System.out.println("Successfully connected to MQ Queue Manager and created queue.");
System.out.println("\nPutting and Getting messages to the Queue...");
for (String msg: msgs){
producer = context.createProducer();
consumer = context.createConsumer(destination);
// Send a message
TextMessage sendMessage = context.createTextMessage(msg);
producer.send(destination, sendMessage);
System.out.println("Sent message: " + sendMessage.getText());
// Recieve a message
TextMessage receivedMessage = (TextMessage) consumer.receive(10000);
if (receivedMessage != null){
System.out.println("Received message: " + receivedMessage.getText());
} else {
System.out.println("error: no message received?!");
System.exit(1);
}
}
} catch (JMSException ex) {
System.out.println("error JMSException occurred: " + ex.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
// getCognitoAccessToken, retrieves an access token from AWS Cognito using provided credentials.
// It constructs a request, sends it to Cognito, and extracts the access token from the response.
private static String getCognitoAccessToken(){
System.out.println("\nGetting user access token from Amazon AWS Cognito...");
String accessToken = "";
String requestData = "{" +
" \"AuthParameters\": {" +
" \"USERNAME\": \"" + username + "\"," +
" \"PASSWORD\": \"" + password + "\"" +
" }," +
" \"AuthFlow\": \"USER_PASSWORD_AUTH\"," +
" \"ClientId\": \"" + clientId + "\"" +
"}";
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://cognito-idp." + region + ".amazonaws.com/"))
.POST(BodyPublishers.ofString(requestData))
.setHeader("X-Amz-Target", "AWSCognitoIdentityProviderService.InitiateAuth")
.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-amz-json-1.1")
.build();
System.out.println("Cognito Request: " + request + requestData);
try{
HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
String JWT = response.body();
Pattern accessTokenPattern = Pattern.compile("\"AccessToken\"\s*:\s*\"([^,]*)\",");
Matcher accessTokenMatcher = accessTokenPattern.matcher(JWT);
if (accessTokenMatcher.find()) {
accessToken = accessTokenMatcher.group(1);
System.out.println("Cognito Access Token: " + accessToken);
} else {
System.out.println("error: Could not parse JWT token response");
System.exit(1);
}
} catch(IOException ex){
System.out.println(ex.toString());
System.exit(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
return accessToken;
}
// getEnvVars, loads environment variables from env.json.
private static void getEnvVars(){
String filename = "env.json";
System.out.printf("Loading environment variables from %s...\n", filename);
String envs = readFile(filename);
System.out.println("MQ Config:");
queueManager = getVar(envs, "QMGR");
queueName = getVar(envs, "QUEUE_NAME");
channel = getVar(envs, "CHANNEL");
String portStr = getVar(envs, "PORT");
try{
port = Integer.parseInt(portStr);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.printf("error: port value provided [%s] is not a number: %s", portStr, e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
System.out.println("\nCognito Config:");
username = getVar(envs, "USERNAME");
password = getVar(envs, "PASSWORD");
clientId = getVar(envs, "CLIENT_ID");
region = getVar(envs, "REGION");
}
// getVar, retrieves the value of a specific environment variable from a JSON-formatted string.
// If the variable is found, it returns its value; otherwise, it prints an error message and exits the program.
private static String getVar(String envs, String name){
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\"" + name + "\"\s*:\s*\"([^,]*)\"");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(envs);
if (matcher.find()) {
String var = matcher.group(1);
if (var == ""){
System.out.println("error: value of " + name + ", is a empty string.");
System.exit(1);
}
System.out.printf(" - %s: \t%s\n", name, var);
return var;
} else {
System.out.println("error: Could not find env var " + name + ", check JSON format is correct and variable isn't missing.");
System.exit(1);
}
return "";
}
// Readfile, reads contents of filename and retuns the file content as a String.
// If error occurs, prints the eror and exits the program.
private static String readFile(String filename) {
try {
return new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(filename)));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.printf("error: failed to read file [%s]: %s", filename, e.toString());
System.exit(1);
return null;
}
}
}
There are two methods to the running the applicaiton, either execute the java commands manually or use the optional Makefile.
You can pass custom messages to MQ by passing command line args after the message e.g. java ... app.mq test-message test-message-2.
Run the app manually:
When inside the MQClient directory run the following javac build command whuch will create app.class inside /app directory:
javac -cp ./com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar:./jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar:./json-20250107.jar app/mq.java
To run the application use the following command:
java -cp ./com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar:./jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar:./json-20250107.jar:. app.mq
Run the app using the Makefile:
Create a file named Makefile in the MQClient directory, and use make run to send a default message or make run m1=test1 m2=test2 m3=test3 m4=test4 m5=test5 to send custom messages, adding more mX variables if you want additional messages.
Note: None of the mX variables are requried, so you can simply m make run m1=test-custom-message or them entirely and it will still work.
.PHONY: run
run: build run-app
.PHONY: build
build:
javac -cp ./com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar:./jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar:./json-20250107.jar app/mq.java
.PHONY: run-app
run-app:
java -cp ./com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar:./jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar:./json-20250107.jar:. app.mq $(m1) $(m2) $(m3) $(m4) $(m5)
.PHONY: clean
clean:
rm -f app/mq.class
Default message
or custom
make run m1=test1 m2=test2 m3=test3 m4=test4 m5=test5
If you followed the example and used the default message you should expect the following output:
[root@aws-cognito-jwks-guide1 MQclient]# make run
rm -f app/mq.class
javac -cp ./com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar:./jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar:./json-20250107.jar app/mq.java
java -cp ./com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar:./jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar:./json-20250107.jar:. app.mq
Java Jakarta App to send message to MQ with AWS Cognito providing JWKS Authentication.
Loading environment variables from env.json...
MQ Config:
- QMGR: QM1
- QUEUE_NAME: DEV.QUEUE.1
- CHANNEL: DEV.APP.SVRCONN
- PORT: 1414
Cognito Config:
- USERNAME: app
- PASSWORD: P@ssw0rd1
- CLIENT_ID: 45r7hahlvntu2mrrgkc0di8of3
- REGION: eu-west-2
Getting user access token from Amazon AWS Cognito...
Cognito Request: https://cognito-idp.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/ POST{ "AuthParameters": { "USERNAME": "app", "PASSWORD": "P@ssw0rd1" }, "AuthFlow": "USER_PASSWORD_AUTH", "ClientId": "45r7hahlvntu2mrrgkc0di8of3"}
Cognito Access Token: eyJraWQiOiI1ZjZqQnRnQlRGdFZuVmZjRnZMVWVXdHpvMHRMWUg1eFZkYm03VzBDMU00PSIsImFsZyI6IlJTMjU2In0.eyJzdWIiOiI4NjAyODI5NC01MDYxLTcwZGYtYjIyZi04ZWZkMTY2MTIwYTYiLCJpc3MiOiJodHRwczpcL1wvY29nbml0by1pZHAuZXUtd2VzdC0yLmFtYXpvbmF3cy5jb21cL2V1LXdlc3QtMl9wcUJYQW45alIiLCJjbGllbnRfaWQiOiI0NXI3aGFobHZudHUybXJyZ2tjMGRpOG9mMyIsIm9yaWdpbl9qdGkiOiJhZTg1M2Y5Ny01YjgyLTRiMzYtYjY3Yi04YjFkM2RjOWQ0YmUiLCJldmVudF9pZCI6IjgzNDc1NzE2LTAzMmYtNDRmYy1hZjI5LTEyMzQ1NjQ3YzdkYyIsInRva2VuX3VzZSI6ImFjY2VzcyIsInNjb3BlIjoiYXdzLmNvZ25pdG8uc2lnbmluLnVzZXIuYWRtaW4iLCJhdXRoX3RpbWUiOjE3NTM3MDg4NjgsImV4cCI6MTc1MzcxMjQ2OCwiaWF0IjoxNzUzNzA4ODY4LCJqdGkiOiIyMjMwNTUyZS1kYjRiLTRkNjQtYTVlMS0wMmEwMDgzYzFkZTEiLCJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ImFwcCJ9.F8yYqszWqEsiRC6qie0hSAWUTIjGunwOJsMD0ksAOkmzobAl2By58yXGPswQoGYyYVcMLEGkWFKPAQLLsfiskUDzT--Xpv93KPr8qrCrJT6C6Pwt7ntsUu2Jak9li2pKGIqhw80M5lltZi-xIeGvaIMF3PPrxegEK6smMTzeIoUubWEd5TZcBChDMZJkACqKNARNEQXjrpWXV1WvN4BisLwMDTGpsJh2Tw06dlVNgVSTH5zaXwMOeoL6tcIpbO5_y5uVYG5iUDvsVzBSUQZrSr8YwUHFc5mLqv9rQDRXUzLMakHNyjW7EWU5NQlXt8aJPpvDpCE7ZbhKWgRhvhZiOA
Connecting to MQ...
No arg messages found, using default test message.
Creating connection factory.
Successfully connected to MQ Queue Manager and created queue.
Putting and Getting messages to the Queue...
Sent message: Hello from MQ using AWS Cognito JWKS Token Authtentication!
Received message: Hello from MQ using AWS Cognito JWKS Token Authtentication!
Successfully completed MQ Cognito JWKS validation test.
To prove JWKS Authentication is working:
- Take your latest Access Token.
- Find the line
String accessToken = getCognitoAccessToken();
- Replace that line with
String accessToken = "\<latest-access-token>";
- Remove the last character with a different one to create an invalid access token.
- Build and run the application.
Execpted Output:
Terminal Output:
Java Jakarta App to send message to MQ with AWS Cognito providing JWKS Authentication.
Loading environment variables from env.json...
MQ Config:
- QMGR: QM1
- QUEUE_NAME: DEV.QUEUE.1
- CHANNEL: DEV.APP.SVRCONN
- PORT: 1414
Cognito Config:
- USERNAME: app
- PASSWORD: P@ssw0rd1
- CLIENT_ID: 1e5rmv31d50121p2b7c63299tn
- REGION: eu-west-2
Connecting to MQ...
Creating connection factory.
Exception in thread "main" com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.jms.DetailedJMSSecurityRuntimeException: JMSWMQ2013: The security authentication was not valid that was supplied for queue manager 'QM1' with connection mode 'Client' and host name 'localhost(1414)'.
Please check if the supplied username and password are correct on the queue manager to which you are connecting. For further information, review the queue manager error logs and the Securing IBM MQ topic within IBM Documentation.
at com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.jms.DetailedJMSSecurityException.getUnchecked(DetailedJMSSecurityException.java:270)
at com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.jms.internal.JmsErrorUtils.convertJMSException(JmsErrorUtils.java:173)
at com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.jms.admin.JmsConnectionFactoryImpl.createContext(JmsConnectionFactoryImpl.java:515)
at app.mq.connectAndTestMQ(mq.java:107)
at app.mq.main(mq.java:74)
Caused by: com.ibm.mq.MQException: JMSCMQ0001: IBM MQ call failed with compcode '2' ('MQCC_FAILED') reason '2035' ('MQRC_NOT_AUTHORIZED').
at com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.wmq.common.internal.Reason.createException(Reason.java:203)
at com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.wmq.internal.WMQConnection.<init>(WMQConnection.java:505)
at com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.wmq.factories.WMQConnectionFactory.createV7ProviderConnection(WMQConnectionFactory.java:9112)
at com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.wmq.factories.WMQConnectionFactory.createProviderConnection(WMQConnectionFactory.java:8452)
at com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.jms.admin.JmsConnectionFactoryImpl._createConnection(JmsConnectionFactoryImpl.java:322)
at com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.jms.admin.JmsConnectionFactoryImpl.createContext(JmsConnectionFactoryImpl.java:481)
... 2 more
Queue Manager Error Logs:
Read the latest MQ error logs inside the AMQERRO1.LOG:
podman exec -it QM1 bash
cat /var/mqm/qmgrs/QM1/errors/AMQERR01.LOG
MQ error Logs output:
07/29/25 08:25:19 - Process(1548.20) User(mqm) Program(amqzlaa0)
Host(afc3e0a126eb) Installation(Installation1)
VRMF(9.4.3.0) QMgr(QM1)
Time(2025-07-29T08:25:19.568Z)
ArithInsert1(106)
CommentInsert1(app.mq)
AMQ5784E: Authentication token cannot be validated. Error code=106.
EXPLANATION:
The authentication token provided by the 'app.mq' program cannot be validated.
The error code in the message indicates the cause of the failure.
The claim that caused the failure is ''.
The value of the claim that caused the failure is ''.
ACTION:
Use the error code in the message to understand why the token could not be
validated. Refer to the 'Token authentication error codes' topic in the IBM MQ
documentation for a list of error codes and their meaning. Correct the error,
then re-run the application.
----- amqzfuca.c : 4799 -------------------------------------------------------
Congratulations! In this guide, you've learned to create an AWS Cognito User Pool, register users, and authenticate them. You also configured an IBM MQ Queue Manager for token-based authentication. Finally, you connected a Java Jakarta application to the queue manager, enabling it to send and receive messages to a queue using the Cognito Access Token.
Script to install and create everything required for the Jakarta MQ App with Cognito JWKS-based-authentication.
Note: Make sure you add your client_id to the env.json file and double all other credentials are correct.
echo "Creating MQ Jakarta Application and installing dependencies..."
# Tidy existing files.
rm -rf MQClient
# Make the necessary directories and install the relevant java dependencies.
mkdir MQClient
cd MQClient
curl -o com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/ibm/mq/com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client/9.4.2.0/com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar
curl -o jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/jakarta/jms/jakarta.jms-api/3.1.0/jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar
curl -o json-20250107.jar https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/json/json/20250107/json-20250107.jar
mkdir app
# Create the json env file.
cat <<EOF > env.json
{
"MQ_CONFIG": {
"QMGR": "QM1",
"QUEUE_NAME": "DEV.QUEUE.1",
"CHANNEL": "DEV.APP.SVRCONN",
"PORT": "1414"
},
"COGNITO_CONFIG": {
"USERNAME": "app",
"PASSWORD": "P@ssw0rd1",
"CLIENT_ID": "",
"REGION": "eu-west-2"
}
}
EOF
echo "env.json created with the following content:"
cat env.json
# Create the Makefile.
cat <<EOF > Makefile
.PHONY: run
run: build run-app
.PHONY: build
build:
javac -cp ./com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar:./jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar:./json-20250107.jar app/mq.java
.PHONY: run-app
run-app:
java -cp ./com.ibm.mq.jakarta.client-9.4.2.0.jar:./jakarta.jms-api-3.1.0.jar:./json-20250107.jar:. app.mq \$(m1) \$(m2) \$(m3) \$(m4) \$(m5)
.PHONY: clean
clean:
rm -f app/mq.class
EOF
echo "Makefile created with the following content:"
cat Makefile
# Create the Java Jakarta MQ app.
cd app
cat <<EOF > mq.java
package app;
import jakarta.jms.Destination;
import jakarta.jms.JMSConsumer;
import jakarta.jms.JMSProducer;
import jakarta.jms.JMSContext;
import jakarta.jms.JMSException;
import jakarta.jms.TextMessage;
import com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.jms.JmsConnectionFactory;
import com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.jms.JmsFactoryFactory;
import com.ibm.msg.client.jakarta.wmq.WMQConstants;
import com.ibm.mq.constants.MQConstants;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest.BodyPublishers;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class mq {
// MQ Queue Manager Configuration.
private static String queueManager = "";
private static String queueName = "";
private static String channel = "";
private static int port = 0;
// Cognito JWKS Configuration.
private static String username = "";
private static String password = "";
private static String clientId = "";
private static String region = "";
/*
Purpose: This Java application demonstrates how to send and receive messages to/from an IBM MQ queue using
AWS Cognito for JWKS-based authentication.
Dependencies:
- Jakarta Messaging API (JMS) for MQ interaction.
- IBM MQ Java client libraries.
- AWS SDK for Java (specifically, HttpClient for Cognito token retrieval).
Configuration:
Environment variables for MQ connection details (queue manager, queue name, channel, port) and Cognito configuration details
(username, password, client ID, region) are loaded from the `env.json` file.
Flow:
- The application loads environment variables from env.json.
- Retrives an access token from AWS Cognito using the provided credentials and the HTTP package.
- Connects to the MQ queue and sends/receives messages specified by the arguments.
- After successful message exchange, it prints a success message and exits.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("\nJava Jakarta App to send message to MQ with AWS Cognito providing JWKS Authentication.\n");
// Load environment variables from env.json.
getEnvVars();
// Obtain access token from Cognito.
String accessToken = getCognitoAccessToken();
System.out.println("\nConnecting to MQ...");
if (args.length > 0) {
// Connect to MQ and use the command line arguments to send custom messages.
connectAndTestMQ(accessToken, args);
} else {
// Use default message if no arguments are provided
System.out.println("No arg messages found, using default test message.");
String[] msgs = {"Hello from MQ using AWS Cognito JWKS Token Authtentication!"};
// Connect to MQ using the defualt message.
connectAndTestMQ(accessToken, msgs);
}
System.out.println("\nSuccessfully completed MQ Cognito JWKS validation test.");
// Expected end of execution.
System.exit(0);
}
// connectAndTestMQ, establishes a connection to an MQ queue using provided credentials and sends/receives messages.
private static void connectAndTestMQ(String accessToken, String[] msgs){
JMSContext context = null;
Destination destination = null;
JMSProducer producer = null;
JMSConsumer consumer = null;
try {
System.out.println("Creating connection factory.");
JmsFactoryFactory ff = JmsFactoryFactory.getInstance(WMQConstants.JAKARTA_WMQ_PROVIDER);
JmsConnectionFactory cf = ff.createConnectionFactory();
// Set MQ connection properties.
cf.setIntProperty(WMQConstants.WMQ_CONNECTION_MODE, WMQConstants.WMQ_CM_CLIENT);
cf.setIntProperty(WMQConstants.WMQ_PORT, port);
cf.setStringProperty(WMQConstants.WMQ_CHANNEL, channel);
cf.setStringProperty(WMQConstants.WMQ_QUEUE_MANAGER, queueManager);
// Use the Cognito access token for authentication.
cf.setStringProperty(WMQConstants.PASSWORD, accessToken);
context = cf.createContext();
destination = context.createQueue("queue:///" + queueName);
System.out.println("Successfully connected to MQ Queue Manager and created queue.");
System.out.println("\nPutting and Getting messages to the Queue...");
for (String msg: msgs){
producer = context.createProducer();
consumer = context.createConsumer(destination);
// Send a message
TextMessage sendMessage = context.createTextMessage(msg);
producer.send(destination, sendMessage);
System.out.println("Sent message: " + sendMessage.getText());
// Recieve a message
TextMessage receivedMessage = (TextMessage) consumer.receive(10000);
if (receivedMessage != null){
System.out.println("Received message: " + receivedMessage.getText());
} else {
System.out.println("error: no message received?!");
System.exit(1);
}
}
} catch (JMSException ex) {
System.out.println("error JMSException occurred: " + ex.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
// getCognitoAccessToken, retrieves an access token from AWS Cognito using provided credentials.
// It constructs a request, sends it to Cognito, and extracts the access token from the response.
private static String getCognitoAccessToken(){
System.out.println("\nGetting user access token from Amazon AWS Cognito...");
String accessToken = "";
String requestData = "{" +
" \"AuthParameters\": {" +
" \"USERNAME\": \"" + username + "\"," +
" \"PASSWORD\": \"" + password + "\"" +
" }," +
" \"AuthFlow\": \"USER_PASSWORD_AUTH\"," +
" \"ClientId\": \"" + clientId + "\"" +
"}";
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://cognito-idp." + region + ".amazonaws.com/"))
.POST(BodyPublishers.ofString(requestData))
.setHeader("X-Amz-Target", "AWSCognitoIdentityProviderService.InitiateAuth")
.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-amz-json-1.1")
.build();
System.out.println("Cognito Request: " + request + requestData);
try{
HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
String JWT = response.body();
Pattern accessTokenPattern = Pattern.compile("\"AccessToken\"\s*:\s*\"([^,]*)\",");
Matcher accessTokenMatcher = accessTokenPattern.matcher(JWT);
if (accessTokenMatcher.find()) {
accessToken = accessTokenMatcher.group(1);
System.out.println("Cognito Access Token: " + accessToken);
} else {
System.out.println("error: Could not parse JWT token response");
System.exit(1);
}
} catch(IOException ex){
System.out.println(ex.toString());
System.exit(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
return accessToken;
}
// getEnvVars, loads environment variables from env.json.
private static void getEnvVars(){
String filename = "env.json";
System.out.printf("Loading environment variables from %s...\n", filename);
String envs = readFile(filename);
System.out.println("MQ Config:");
queueManager = getVar(envs, "QMGR");
queueName = getVar(envs, "QUEUE_NAME");
channel = getVar(envs, "CHANNEL");
String portStr = getVar(envs, "PORT");
try{
port = Integer.parseInt(portStr);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.printf("error: port value provided [%s] is not a number: %s", portStr, e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
System.out.println("\nCognito Config:");
username = getVar(envs, "USERNAME");
password = getVar(envs, "PASSWORD");
clientId = getVar(envs, "CLIENT_ID");
region = getVar(envs, "REGION");
}
// getVar, retrieves the value of a specific environment variable from a JSON-formatted string.
// If the variable is found, it returns its value; otherwise, it prints an error message and exits the program.
private static String getVar(String envs, String name){
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\"" + name + "\"\s*:\s*\"([^,]*)\"");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(envs);
if (matcher.find()) {
String var = matcher.group(1);
if (var == ""){
System.out.println("error: value of " + name + ", is a empty string.");
System.exit(1);
}
System.out.printf(" - %s: \t%s\n", name, var);
return var;
} else {
System.out.println("error: Could not find env var " + name + ", check JSON format is correct and variable isn't missing.");
System.exit(1);
}
return "";
}
// Readfile, reads contents of filename and retuns the file content as a String.
// If error occurs, prints the eror and exits the program.
private static String readFile(String filename) {
try {
return new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(filename)));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.printf("error: failed to read file [%s]: %s", filename, e.toString());
System.exit(1);
return null;
}
}
}
EOF
echo "mq.java created with the following content:"
cat mq.java
cd ..
echo "Setup of MQ Jakarta app is complete."