Originally posted by: Steve Haertel
Sometimes users want their services to use virtual IPs so that they can be accessed in the same way no matter where they exist. EGO services have the ability to run using virtual IPs, but in IBM Spectrum Conductor with Spark 2.2.1, we have streamlined the process to do so for the Spark master batch and history services so that users do not have to manually edit their service profiles.
We introduced four new Spark configuration parameters for configuring virtual IPs: spark.masterbatch.basevirtualip, spark.masterbatch.virtualipnetmask, spark.history.basevirtualip, and spark.history.virtualipnetmask.
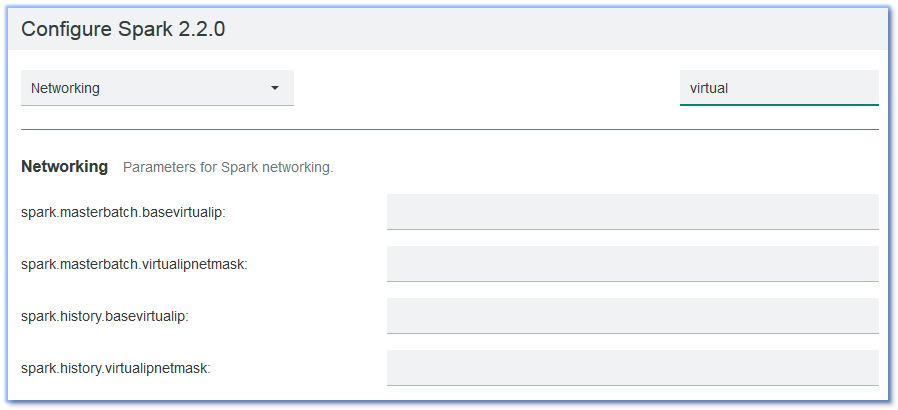
When users set these parameter values, their corresponding EGO services automatically receive the correct service profile additions.
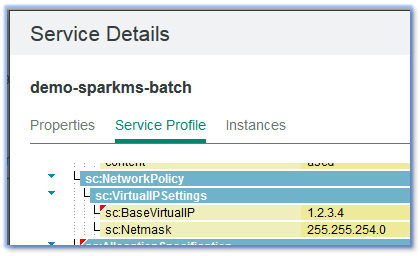
If a service is scaled, the new service instances receive virtual IP addresses that start at the base address, and increase according to the netmask value.
With your Spark master batch service configured with a virtual IP, you can submit Spark applications through RESTful APIs using the virtual IP, or a virtual host name (the host name that is attached to the virtual IP):
curl -X POST -k -u username:a https://[VIRTUAL_IP]:6067/v1/submissions/create --header 'Content-Type:application/json' --header 'Accept:application/json' --data '{ {"action" : "CreateSubmissionRequest","appArgs" : [ "10000" ],"appResource" : "file:/deploy/location/spark-1.6.1-hadoop-2.6/lib/spark-examples-1.6.1-hadoop2.6.0.jar","clientSparkVersion" : "1.6.1","environmentVariables" : {"SPARK_ENV_LOADED" : "1"},"mainClass" : "org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi","sparkProperties" : {"spark.jars" : "file:/deploy/location/spark-1.6.1-hadoop-2.6/lib/spark-examples-1.6.1-hadoop2.6.0.jar","spark.driver.supervise" : "false","spark.app.name" : "Spark Pi","spark.submit.deployMode" : "cluster","spark.master" : "spark:// [VIRTUAL_IP]:6067"}}}'
The following is an example of an application submission through the command line using the virtual host name:
spark-submit --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi --master spark://vhost.domain.com:7077 --deploy-mode cluster --conf spark.ego.uname=Admin --conf spark.ego.passwd=AdminPwd /deploy/location/spark-2.2.0-hadoop-2.7/examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.2.0.jar 10000
You can also use the virtual IP to submit applications through the IBM Spectrum Conductor with Spark RESTful API:
curl -X POST -k -u Admin:AdminPwd https://hostname.domain.com:8643/platform/rest/conductor/v1/instances/da7abf89-a052-49a3-a5d5-6321fb530e3a/applications --header 'Content-Type:application/json' --data '{ "command": "--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi /deploy/location/spark-2.2.0-hadoop-2.7/examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.2.0.jar 10000", "batchmasterresturl": "http://172.29.10.179:6066" }‘
Enabling the virtual IP on the WEBGUI service
- Make sure one available host name can be resolved in DNS and accessed on your local side.
- In your cluster environment, ensure that the virtual host name can be resolved and that the virtual IP is not able to be pinged (meaning it is not already being used).
[root@host~]# nslookup vhost.domain.com
Server: 9.55.55.111
Address: 9.55.55.111#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: vhost.domain.com
Address: 9.55.65.120
[root@host ~]# ping 9.55.65.120
PING 9.55.65.120 (9.111.157.120) 56(84) bytes of data.
From 9.55.64.104 icmp_seq=2 Destination Host Unreachable
From 9.55.64.104 icmp_seq=3 Destination Host Unreachable
- Add an entry to your OS's host file “9.55.65.120 vhost.domain.com”.
- To enable VIP for the WEBGUI, stop the WEBGUI service and edit the WEBGUI service XML file $EGO_ESRVDIR/esc/conf/services/gui_service.xml.
- The HostFailoverInterval value should be the same as the value in the ascd and REST services.
- The Netmask should be the same as the one in the current network environment.
……
<sc:ControlPolicy>
<sc:StartType>AUTOMATIC</sc:StartType>
<sc:MaxRestarts>10</sc:MaxRestarts>
<sc:HostFailoverInterval>PT10S</sc:HostFailoverInterval>
<sc:Dependency type="OnStart">REST</sc:Dependency>
</sc:ControlPolicy>
<sc:NetworkPolicy>
<sc:VirtualIPSettings>
<sc:BaseVirtualIP>9.55.65.120</sc:BaseVirtualIP>
<sc:Netmask>255.255.254.0</sc:Netmask>
</sc:VirtualIPSettings>
</sc:NetworkPolicy>
<sc:AllocationSpecification>
……
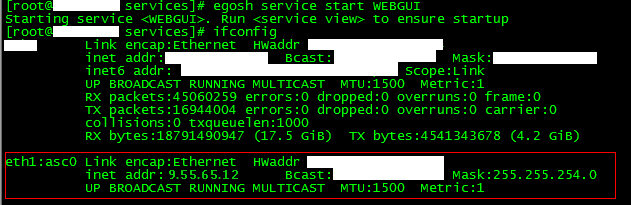
- Verify that the virtual IP has taken effect.
- After updating the WEBGUI service profile, restart the service. You can get the virtual IP via "ifconfig"
- Access the IBM Spectrum Conductor with Spark cluster management console. You can access this at https://vhost.domain.com:8443/platform.
Limitations
An application instance that is configured for virtual IP cannot start
This issue occurs when the name of a network interface (in combination with the internally generated alias name) exceeds the maximum length of 15 characters. To fix this issue, rename the network interface to ensure that its name does not exceed 10 characters.
You can find more information on this limitation here:
If you want to try out IBM Spectrum Conductor with Spark 2.2.1, you can download the evaluation version here.
If you have any questions or comments about using virtual IPs with IBM Spectrum Conductor with Spark 2.2.1, you can post them in our forum or join us on Slack!
#SpectrumComputingGroup