How do you optimize AWS cloud costs? Amazon Web Services offers customers the ability to build modern, scalable applications that help drive digital business success. However, due to its complexity, achieving operational excellence in the cloud is difficult. Fundamentally, as a Cloud Operator, you need to ensure great end-user experiences while staying within budget.
In this post, we’ll give you a quick overview of the various methods of AWS cloud cost management —what problems they solve and how best to leverage them. However, regardless of what cloud cost optimization strategy you employ, achieving operational excellence at scale and taking advantage of the elasticity of the cloud requires software that optimizes your consumption simultaneously for performance and cost—and makes it easy for you to automate it, safely and confidently. Let’s see how IBM Turbonomic helps customers optimize their AWS cloud costs.
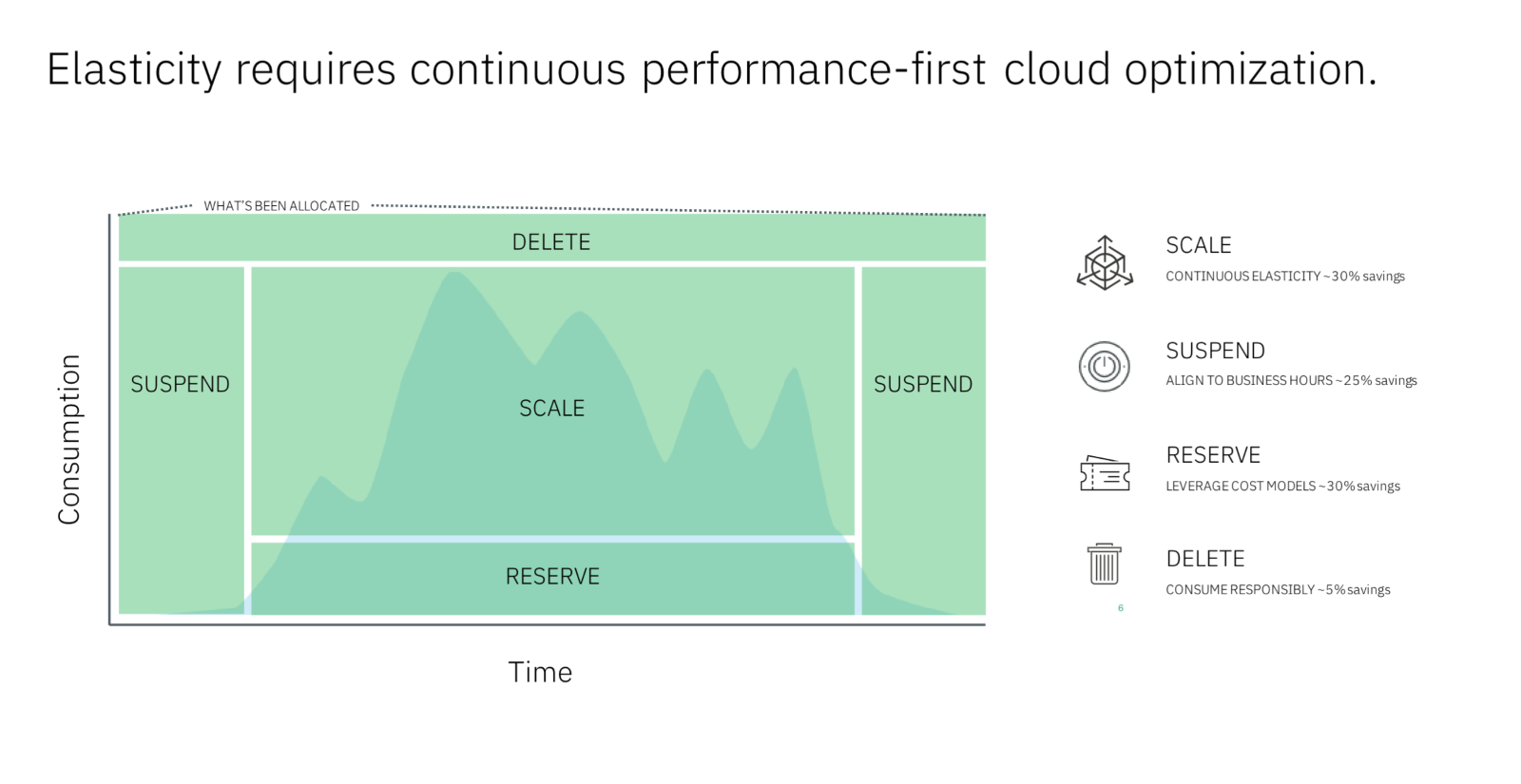
Rightsize EC2 Instances
Amazon Web Services’ operating expense model (OPEX) charges customers for the capacity available for different resources regardless of whether they are fully utilized or not. Customers can purchase instances in different sizes and types, but often default to buying the largest instance available to ensure performance. Rightsizing resources is the process of matching instance types and sizes to workload performance and capacity requirements. To optimize costs, rightsizing resources must be done on a continuous basis, however organizations often rightsize reactively like, for example, after executing a “lift and shift” cloud migration or development.
AWS customers can use AWS Cost Explorer’s rightsizing recommendations to rightsize their EC2 instances, however these recommendations are generated based on historical utilization and do not consider important metrics, such as memory utilization, without leveraging 3rd party monitoring tools or AWS CloudWatch.
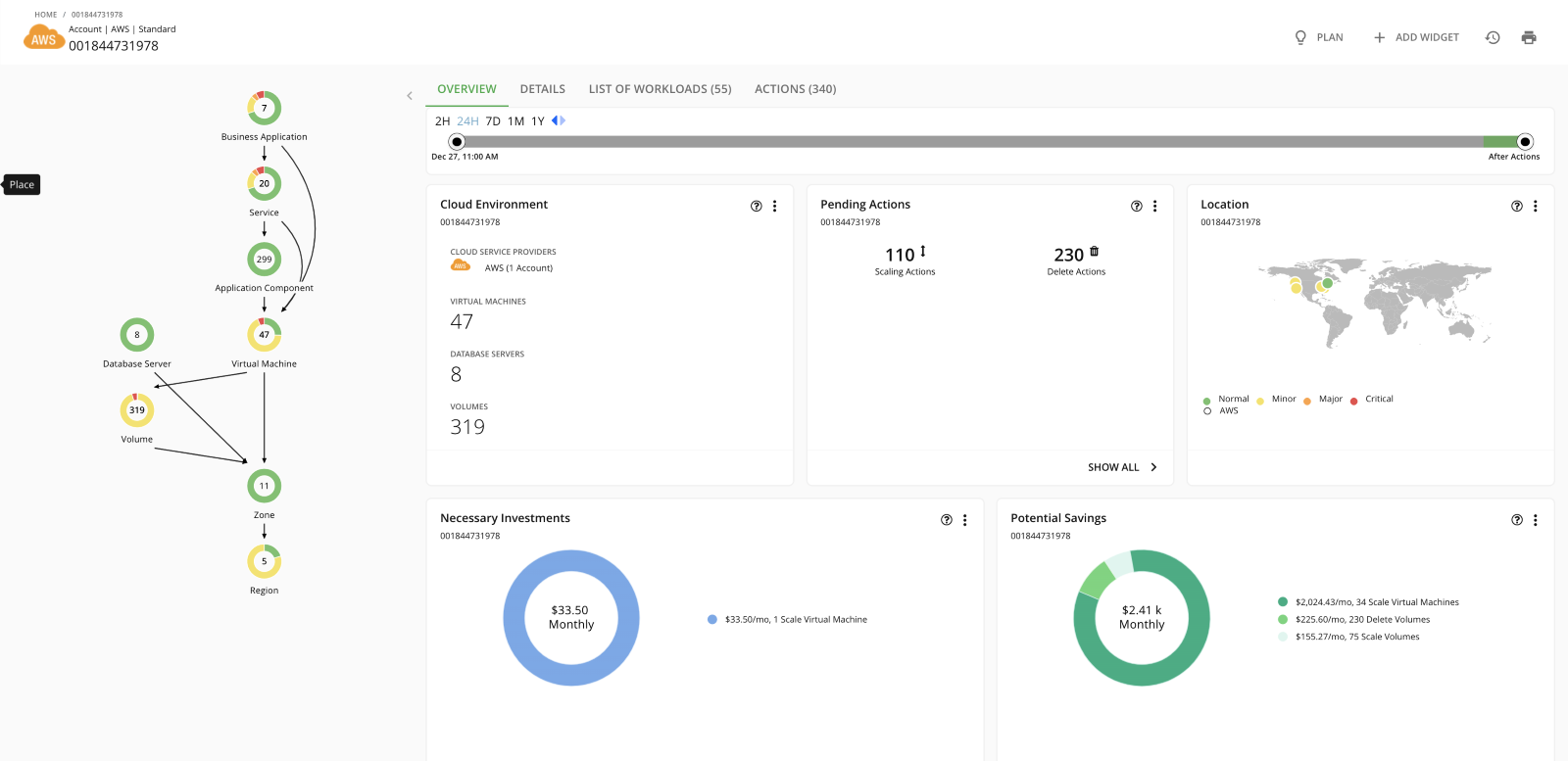
Let’s see how IBM Turbonomic helps customers rightsize EC2 instances through percentile-based scaling. The diagrams below depict the IBM Turbonomic UI. Diagram A shows the application stack. The supply chain on the left represents the resource relationships that Turbonomic maps out from the business application down to the Cloud Region and can include other components such as container pods, storage volumes, virtual machines and more – depending on the infrastructure that supports the application. This full-stack understanding is what makes Turbonomic’s recommendations trustworthy and gives cloud engineer and operations the confidence to automate. For this particular AWS account, Turbonomic has identified 110 pending scaling actions.
Diagram A
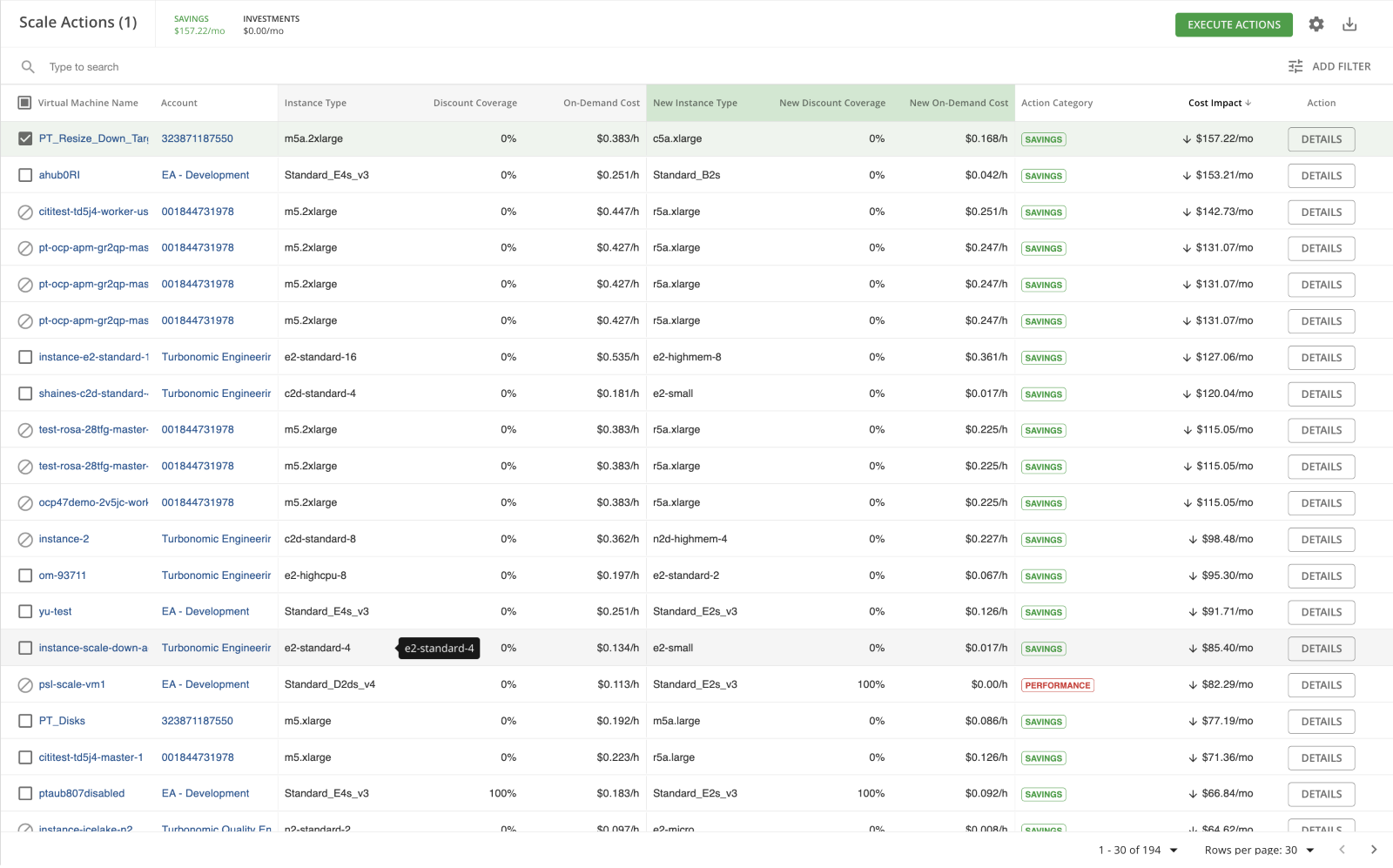
After selecting “SHOW ALL” customers are brought to Turbonomic’s Action Center, which can be found in Diagram B below. This diagram represents all of the scaling actions available for this AWS account. From viewing this dashboard, customers can see important information including the account name, instance type, discount coverage, and on-demand cost. Customers can select different actions and execute them by clicking “EXECUTE ACTIONS” in the top right corner.
Diagram B
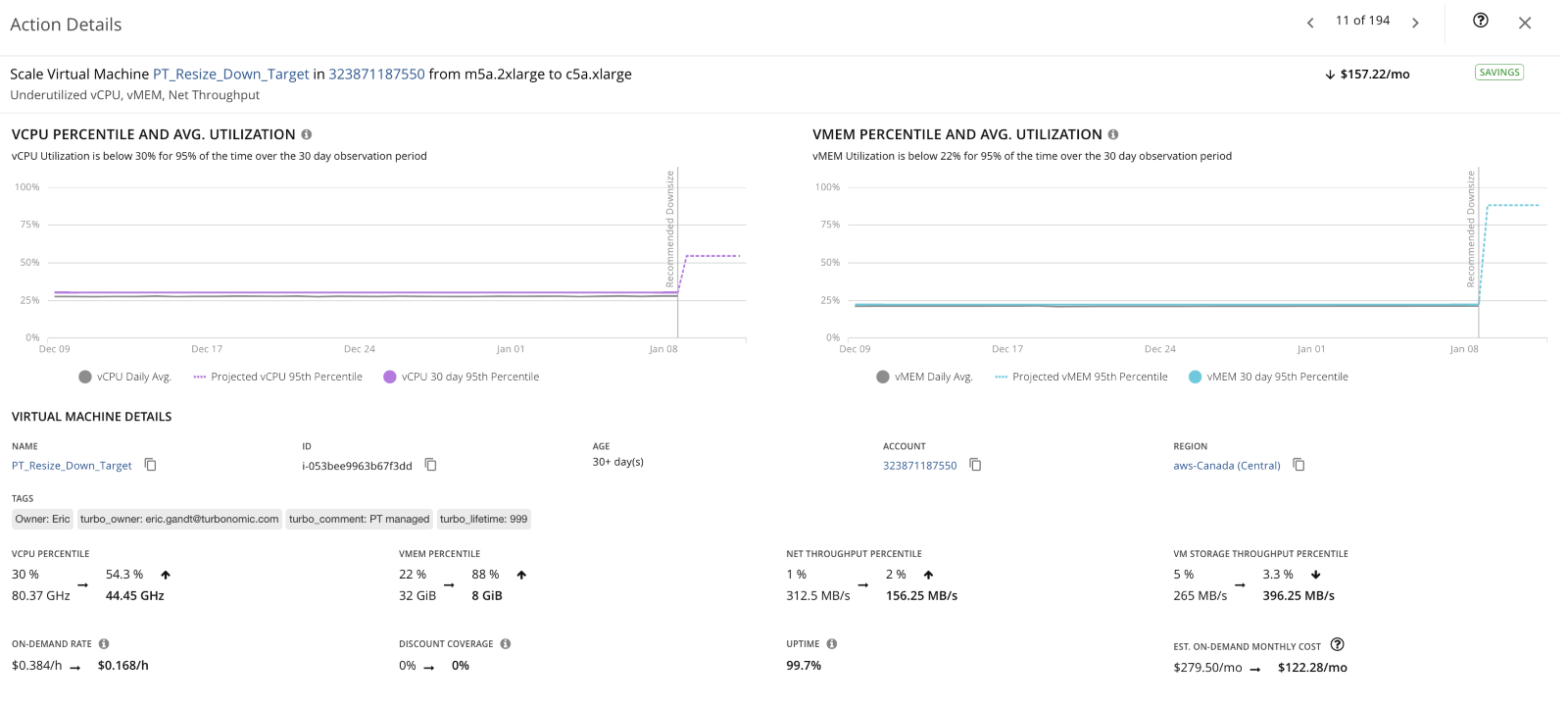
For customers looking for more details on a particular action, they can select “DETAILS” where Turbonomic provides additional information that it considers in its recommendations. As shown below in Diagram C, this instance needs to be scaled down because it has underutilized vCPU, VMem and Net throughput. Other information for this action includes the cost impact of executing the action, the resulting CPU and Memory utilization, uptime and net throughput.
Diagram C
Scale EC2 Instances
Public cloud environments are ephemeral, and to meet budget and performance goals, AWS customers must scale their instances both vertically (rightsizing) and horizontally. To scale horizontally, AWS users must monitor application load balances and then scale out instances as load increases from increased demand. Distributing load across multiple instances through horizontal scaling increases performance and reliability, but instances must be scaled back as demand changes to avoid incurring unnecessary costs. AWS customers can use AWS EC2 Autoscaling to enable horizontally scaling in their environment, however, this tool scales under the constraint of user-defined policies and only for designated EC2 instances called Auto Scaling Groups.
The only way to optimize horizontal scaling is to do it in real time through automation. IBM Turbonomic continuously generates scaling actions so applications can always perform at the lowest cost. Diagram D below represents an AWS account that needs to be scaled out.
Diagram D

The horizontal scaling action for this AWS account can be executed in the Action Center under the “Provision Actions” subcategory found in Diagram E below. Here you can find information on the actions and the corresponding workload such as the container cluster, the namespace, and the risk posed to the workload, which in this case is transaction congestion.
In Diagram F below you can see how Turbonomic provides the rationale behind taking the action, in this case a container pod is experiencing transaction congestions and needs to be provisioned additional CPU to improve performance. Turbonomic also specifies all the container pod details including the name, workload controller, namespace and container cluster.
Diagram F

Have you seen enough? Get started by trying the IBM Turbonomic Sandbox or Request your IBM Turbonomic demo today!
Suspending Idle EC2 Instances
Another impactful way to reduce optimize AWS cloud costs is to shut down idle instances. An organization may suspend instances if it is not currently using the instance, such as during non-business hours, but expects to resume use in the near-term. When deleting an instance, the instance will be shut down and any data stored on the attached EBS volume is also deleted. However, when suspending an instance, customers do not delete the underlying data contained in the attached EBS volume. When starting the instance again, the EBS volume is simply attached to a newly provisioned instance, resulting in faster boot time. AWS CloudWatch can help AWS customers suspend idle EC2 instances. AWS CloudWatch will send an alarm to users when an instance has an average CPU utilization that is below 10% for over 24 hours. Users must define which instances to monitor and their corresponding utilization thresholds.
IBM Turbonomic automatically identifies and provides recommendations for suspending instances. To suspend an instance with Turbonomic, customers will need to first select an AWS account with a pending suspension action as show in Diagram G below.

Diagram H
To execute a suspension action, Turbonomic customers simply needs to go to the action center, select the corresponding action and execute. Under the “Suspend Actions” tab of the Action Center, customers can see the Vmem, VCPU and Vstorage capacity for each instance with a pending action.

If customers need additional details before executing, they can select the “DETAILS” show in the Diagram I below. The details provided for this action include the reasoning behind the action, in this case to improve infrastructure efficiency, as well as the cost impact, age of the instance, the virtual CPU and Memory and the number of consumers for this instance.
Diagram I

Leverage Reserved Instance Discounting
Customers can also leverage discounted pricing through optimizing reserved instance coverage and utilization to reduce costs. AWS Cost Explorer is also the native tool offered for RI purchasing recommendations. Cost Explorer’s recommendations are generated from individual account usage of the previous 60 days. Cost Explorer does not forecast and assumes that historical usage will reflect future usage in its recommendations.
IBM Turbonomic’s analytics engine automatically ingests and displays negotiated rates with public cloud providers and then generates specific reserved instance purchasing and scaling actions so customers can take full advantage of existing RI inventory and maximize reservation-to-instance coverage. Diagram J represents an AWS account that has pending actions to increase RI utilization and coverage.
Diagram J

Diagram K represents the “Buy” actions that can be executed in the action center to increase RI coverage. Some important details listed in the Action Center here are the platform the RI will be purchased on, the term of the RI, the payment type and the region. Diagram L provides more details for this action such as the cost impact and resulting RI coverage. All of this information can again be found in the corresponding “DETAILS” tab.
Diagram K

Diagram L
 For longer term commitments, Turbonomic provides reserved instance planning scenarios for added customization. On the Turbonomic platform, users simply select “PLAN” on the dashboard on the left and then select “NEW PLAN.” After selecting “NEW PLAN,” customers can then select the reservation planning option shown below in Diagram M.
For longer term commitments, Turbonomic provides reserved instance planning scenarios for added customization. On the Turbonomic platform, users simply select “PLAN” on the dashboard on the left and then select “NEW PLAN.” After selecting “NEW PLAN,” customers can then select the reservation planning option shown below in Diagram M.
Diagram M

First, customers need to indicate the scope of the reservation purchasing plan. For this purpose, we are going to select AWS. Turbonomic users can also scope by custom groups, accounts, billing families and regions as shown in Diagram N below.
Diagram N

After indicating the scope of the reservation plan, customers can then configure the plan to the preferred offering class, term and payment type shown below in Diagram O. Customers can also customize the historical usage period they want Turbonomic to analyze as well as whether to use data from deleted VMs.
Diagram O

After running the plan, Turbonomic will provide a dashboard as found in Diagram P. In this plan, customers can see the cloud cost comparison currently versus after executing the plan. This comparison covers RI coverage, RI utilization, on-demand compute cost and reserved compute cost. Turbonomic also provides insight on virtual machine mapping and discount inventory.
Diagram P.

Finally, Turbonomic summarizes all of the actions that will be executed as part of your VM reservation plan. These actions are summarized under the “PLAN ACTIONs” and are shown in Diagram Q below.
Diagram Q

Delete Unattached Resources
Finally, as previously discussed, Amazon Web Services’ operating expense model (OPEX) charges customers not just for the resources that are actively in use, but also for the entire pool of resources available. As organizations build and deploy new releases into their environment, some resources are left unattached. Unattached resources are when customers create a resource, but stops using it entirely. After development, hundreds of different resource types can be left unattached Deleting unattached resources can significantly reduce wasted cloud expenditure. Diagram R below shows an AWS account that has identified 230 unattached resources that can be removed. Similar to suspending idle instances, AWS CloudWatch also allows customers to delete EC2 instances. Just as with instance suspension, AWS CloudWatch will send an alarm to users to delete an instance based off of utilization thresholds.
Diagram R

The delete actions for this account are listed in the Action Center in Diagram S. The information listed in the “Delete” category of the Action center include the size of the EBS volume, the storage tier, the amount of time it has been unattached and the cost impact of removing it.
Diagram S 
For additional insight on the impact of these delete actions, again customers can select the “DETAILS” tab and find more information as shown in Diagram T. Below you can the purpose of this action is to increase savings. Customers can also see additional information such as the volume details, whether the action is disruptive, the resource and cost impact.
Diagram T 
Trustworthy automation is the best way to maximize business value on AWS
For cloud engineering and operations teams looking to achieve budget goals without negatively impacting customer experience, IBM Turbonomic offers a proven path that you can trust. Only Turbonomic can analyze your AWS environment and continuously match real-time application demand to AWS’ unprecedented number of configuration options across EC2 compute, EBS volumes storage, AWS RDS databases and existing savings inventory. Are you looking to reduce spend across your AWS environment as soon as possible? IBM Turbonomic’s automation can be operationalized, allowing teams to see tangible results immediately and continuously, while achieving 471% ROI in less than six months.*
Turbonomic can help you make sure you’re picking the best options in your cloud journey. Get started by trying the IBM Turbonomic Sandbox or Request your IBM Turbonomic demo today!
*Read the Forrester Consulting commissioned study to see what outcomes our customers have achieved with IBM Turbonomic.