Instagocb is the latest tracer package from IBM Instana. It provides interfaces and methods designed to instrument Golang application code with the Couchbase SDK (gocb).
For more information on Instagocb, refer to Instana instrumentation of Couchbase SDK v2 (gocb) for Go
Couchbase is one of the industry’s top NoSQL databases, offering numerous advantages in comparison with popular alternatives such as MongoDB and DynamoDB. The primary benefits include auto-sharding, an integrated cache engine, and support for the SQL-like query language N1QL.
This blog covers instrumenting the Couchbase Go SDK and using it in your Go application to trace Couchbase operations.
The beginning!
Instrumenting GOCB looks very easy at first glance as Couchbase provides a gocb.RequestTracer and gocb.RequestSpan interfaces. All you need to do is provide an Instana-specific implementation of these interfaces, and your tracer will be ready. And all our customer has to do is pass this implementation (instagocb.RequestTracer)to the connection options, and tracing will be enabled for all operations.
Life would be too easy if everything were this simple, right? 😄
What might go wrong with this type of implementation?
- Errors are not traced
The native tracer interface provided by GOCB does not support tracing errors. For example, if you call a collection.Query method and expect that the tracer is already injected into the connection; all it does is create a span for that query operation. Even before executing the actual operation, the span ends. In Instana, the existing .NET and Node.js tracers for Couchbase supports tracing errors. So, this implementation is not viable, as the Go tracer for Couchbase also needs to support tracing errors.
- Transactions are not traced
The in-built tracer interface in GOCB does not support tracing Transaction operations.
Solution : Manually instrument Couchbase SDK
Manually instrumenting the Couchbase SDK is the only way to overcome these issues.
An interface is provided for every instrumented service in GOCB. Use this interface instead of using the direct instances from GOCB.
For example, instead of *gocb.Cluster, use instagocb.Cluster interface, and *gocb.Collection becomes instagocb.Collection. This applies to all instrumented services.
The underlying implementation for each of these interfaces can be put into a pseudo code:
- Create a span.
- Add attributes to the span (e.g., bucket name, operation name, etc.).
- Perform the original operation.
- Add the error from step 3 to the span.
- Finish the span (send the span to the backend).
For example, the interface for *gocb.Collection is shown in the following snippet,
type Collection interface {
Bucket() Bucket
Name() string
QueryIndexes() *gocb.CollectionQueryIndexManager
Do(ops []gocb.BulkOp, opts *gocb.BulkOpOptions) error
Insert(id string, val interface{}, opts *gocb.InsertOptions) (mutOut *gocb.MutationResult, errOut error)
Upsert(id string, val interface{}, opts *gocb.UpsertOptions) (mutOut *gocb.MutationResult, errOut error)
Replace(id string, val interface{}, opts *gocb.ReplaceOptions) (mutOut *gocb.MutationResult, errOut error)
Get(id string, opts *gocb.GetOptions) (docOut *gocb.GetResult, errOut error)
Exists(id string, opts *gocb.ExistsOptions) (docOut *gocb.ExistsResult, errOut error)
GetAllReplicas(id string, opts *gocb.GetAllReplicaOptions) (docOut *gocb.GetAllReplicasResult, errOut error)
GetAnyReplica(id string, opts *gocb.GetAnyReplicaOptions) (docOut *gocb.GetReplicaResult, errOut error)
Remove(id string, opts *gocb.RemoveOptions) (mutOut *gocb.MutationResult, errOut error)
GetAndTouch(id string, expiry time.Duration, opts *gocb.GetAndTouchOptions) (docOut *gocb.GetResult, errOut error)
GetAndLock(id string, lockTime time.Duration, opts *gocb.GetAndLockOptions) (docOut *gocb.GetResult, errOut error)
Unlock(id string, cas gocb.Cas, opts *gocb.UnlockOptions) (errOut error)
Touch(id string, expiry time.Duration, opts *gocb.TouchOptions) (mutOut *gocb.MutationResult, errOut error)
Binary() BinaryCollection
List(id string) CouchbaseList
Map(id string) CouchbaseMap
Set(id string) CouchbaseSet
Queue(id string) CouchbaseQueue
LookupIn(id string, ops []gocb.LookupInSpec, opts *gocb.LookupInOptions) (docOut *gocb.LookupInResult, errOut error)
MutateIn(id string, ops []gocb.MutateInSpec, opts *gocb.MutateInOptions) (mutOut *gocb.MutateInResult, errOut error)
ScopeName() string
Unwrap() *gocb.Collection
}
The underlying implementation is shown in the following snippet:
type instaCollection struct {
*gocb.Collection
iTracer gocb.RequestTracer
}
func (ic *instaCollection) Bucket() Bucket {
bucket := ic.Collection.Bucket()
return createBucket(ic.iTracer, bucket)
}
func (ic *instaCollection) Insert(id string, val interface{}, opts *gocb.InsertOptions) (mutOut *gocb.MutationResult, errOut error) {
var tracectx gocb.RequestSpanContext
if opts.ParentSpan != nil {
tracectx = opts.ParentSpan.Context()
}
span := ic.iTracer.RequestSpan(tracectx, "INSERT")
span.SetAttribute(bucketNameSpanTag, ic.Bucket().Name())
mutOut, errOut = ic.Collection.Insert(id, val, opts)
span.(*Span).err = errOut
defer span.End()
return
}
...
...
...
All the methods except Unwrap() are from the original GOCB-provided struct (*gocb.Collection). Unwrap is a special method exclusively added in the Instagocb library. You will find the Unwrap() method in all Instagocb-provided interfaces, and it will return the underlying GOCB instance.
For example, collection.Unwrap() will return an instance of *gocb.Collection.
func (ic *instaCollection) Unwrap() *gocb.Collection {
return ic.Collection
}
Use Unwrap() if you need the original instance other than the instrumented instance. Even though it is not advisable to use this directly, as Instana tracing will not be enabled if you directly utilise this instance.
How to use Instagocb?
- Instead of using
gocb.Connect, use instagocb.Connect to connect to the Couchbase server. The function definition looks identical, with the exception of the additional argument instana.TraceLogger to instagocb.Connectthat you need to pass.
var collector instana.TracerLogger
collector = instana.InitCollector(&instana.Options{
Service: "sample-app-couchbase",
EnableAutoProfile: true,
})
cluster, err := instagocb.Connect(collector, connectionString, gocb.ClusterOptions{
Authenticator: gocb.PasswordAuthenticator{
Username: username,
Password: password,
},
})
if err != nil {
}
- For every instrumented service, you will find an interface in
instagocb. Use this interface instead of using the direct instances from gocb. For example, instead of *gocb.Cluster, use instagocb.Cluster interface.
- If you use
instagocb.Connect, the returned cluster can provide all the instrumented functionalities. For example, if you use cluster.Buckets(), it will return an instrumented instagocb.BucketManager interface instead of *gocb.BucketManager.
- Set the
ParentSpan property of the options argument using instagocb.GetParentSpanFromContext(ctx) if your Couchbase call is part of an HTTP request. Otherwise, the parent-child relationship of the spans won’t be tracked. It’s demonstrated in the following example.
Example :
var collector instana.TracerLogger
collector = instana.InitCollector(&instana.Options{
Service: "sample-app-couchbase",
EnableAutoProfile: true,
})
cluster, err := instagocb.Connect(collector, connectionString, gocb.ClusterOptions{
Authenticator: gocb.PasswordAuthenticator{
Username: username,
Password: password,
},
})
if err != nil {
}
bucket := cluster.Bucket(bucketName)
err = bucket.WaitUntilReady(5*time.Second, nil)
if err != nil {
}
collection := bucket.Scope("tenant_agent_00").Collection("users")
type User struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Email string `json:"email"`
Interests []string `json:"interests"`
}
_, err = col.Upsert("u:jade",
User{
Name: "Jade",
Email: "jade@test-email.com",
Interests: []string{"Swimming", "Rowing"},
}, &gocb.UpsertOptions{
ParentSpan: instagocb.GetParentSpanFromContext(ctx)
})
if err != nil {
}
Tracing errors
The Instagocb instances trace errors automatically.
Tracing transactions
- Create a new transactions instance by calling
cluster.Transactions(). Like all other instrumented features, this feature also returns an instagocb provided interface (instagocb.Transactions) instead of the original instance (*gocb.Transactions).
- You can use the same
transactions.Run() method to start transactions. Commit, Rollback, and all other transaction-specific things are handled by GOCB. Instana supports tracing on top of transactions.
- In the transaction callback function, go to the first line, call the following method to create an
instagocb instrumented interface of TransactionAttemptContext and use it for the rest of the function to perform all operations such as Insert, Replace, Remove, Get, and Query.
To use the scope or collection inside the transaction function, use the unwrapped instance(scope.Unwrap()) instead of the instagocb interface.
transactions := cluster.Transactions()
_, err = transactions.Run(func(tac *gocb.TransactionAttemptContext) error {
tacNew := cluster.WrapTransactionAttemptContext(tac, instagocb.GetParentSpanFromContext(ctx))
collectionUnwrapped := collection.Unwrap()
_, err := tacNew.Insert(collectionUnwrapped, "doc-a", map[string]interface{}{})
if err != nil {
return err
}
docA, err := tacNew.Get(collectionUnwrapped, "doc-a")
if err != nil {
return err
}
var content map[string]interface{}
err = docA.Content(&content)
if err != nil {
return err
}
content["transactions"] = "are awesome"
_, err = tacNew.Replace(collectionUnwrapped, docA, content)
if err != nil {
return err
}
docA1, err := tacNew.Get(collectionUnwrapped, "doc-a")
if err != nil {
return err
}
err = tacNew.Remove(collectionUnwrapped, docA1)
if err != nil {
return err
}
qr, err := tacNew.Query("SELECT * FROM hotel WHERE country = $1", &gocb.TransactionQueryOptions{
PositionalParameters: []interface{}{"United Kingdom"},
Scope: inventoryScope.Unwrap(),
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
type hotel struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
}
var hotels []hotel
for qr.Next() {
var h hotel
err = qr.Row(&h)
if err != nil {
return err
}
hotels = append(hotels, h)
}
_, err = tacNew.Query("UPDATE route SET airlineid = $1 WHERE airline = $2", &gocb.TransactionQueryOptions{
PositionalParameters: []interface{}{"airline_137", "AF"},
Scope: inventoryScope.Unwrap(),
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}, nil)
var ambigErr gocb.TransactionCommitAmbiguousError
if errors.As(err, &ambigErr) {
log.Println("Transaction possibly committed")
log.Printf("%+v", ambigErr)
return nil
}
var failedErr gocb.TransactionFailedError
if errors.As(err, &failedErr) {
log.Println("Transaction did not reach commit point")
log.Printf("%+v", failedErr)
return nil
}
if err != nil {
return err
}
To see an example of instrumenting a Go application with Instagocb, refer to example/couchbase/main.go
Result
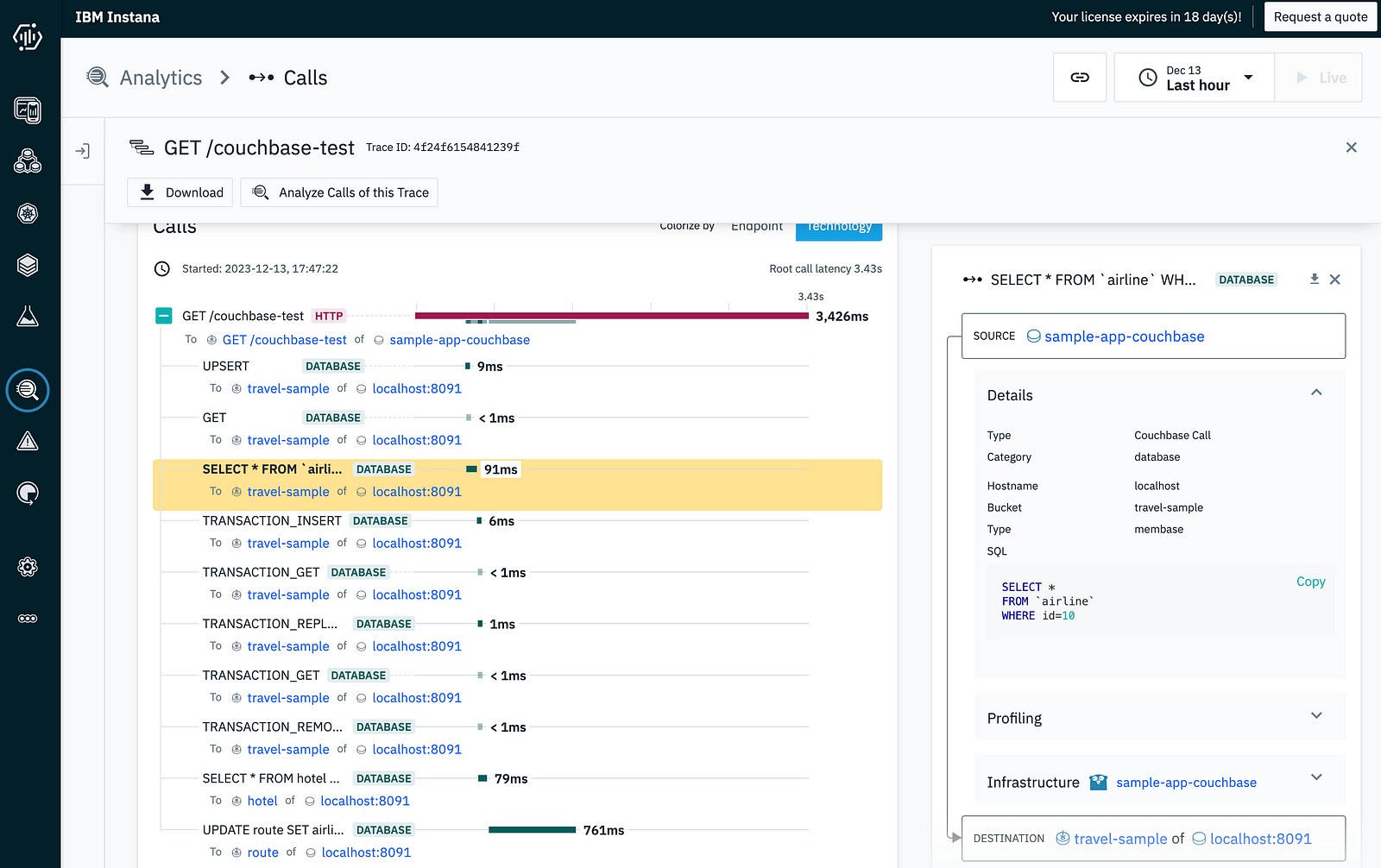
Couchbase tracing and span details are dislayed on the Instana UI.
#Spotlight#Agent