In an era where cyber threats lurk around every virtual corner, safeguarding online assets has become a top priority for businesses and individuals alike. Enter DNSSEC — the unsung hero of internet security!
Let’s delve deeper into this powerful technology and explore why it’s a must-have for anyone serious about protecting their digital presence.
Understanding DNSSEC: A Primer
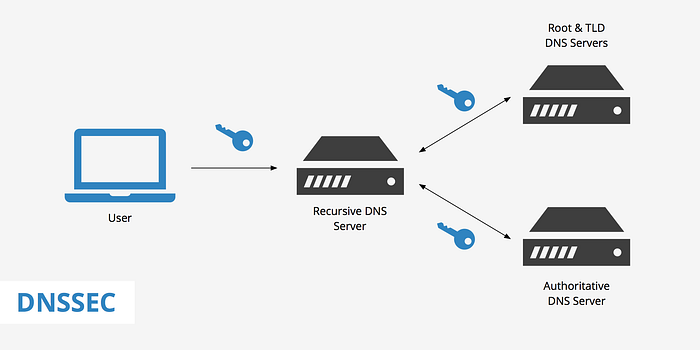
DNSSEC, or Domain Name System Security Extensions, is a set of protocols designed to add an additional layer of security to the Domain Name System (DNS). The traditional DNS system works by using unencrypted data for DNS records, and that’s one of the things that DNSSEC is designed to fix.
At its core, DNSSEC aims to address vulnerabilities within the traditional DNS infrastructure by providing a mechanism for validating the authenticity of DNS data.
Its a set of cryptographic protocols designed to address vulnerabilities within the Domain Name System (DNS). By digitally signing DNS data, DNSSEC ensures the authenticity and integrity of DNS records, mitigating the risk of attacks such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning.
Why DNSSEC Matters: Protecting Your Online Assets
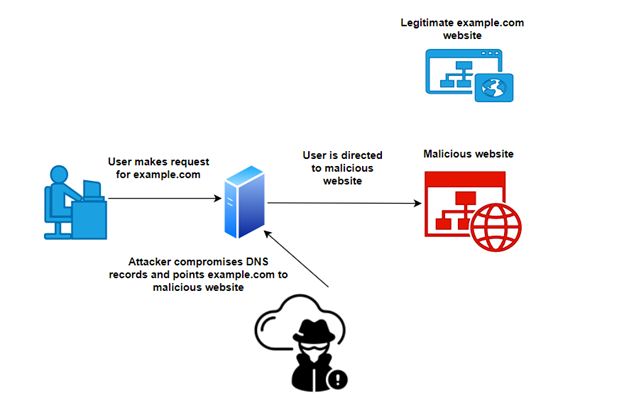
To understand the importance of DNSSEC, you need to know what can happen without it.
In today’s hyper-connected world, the implications of DNS vulnerabilities are far-reaching. From phishing attacks to DNS hijacking, cyber-criminals exploit weaknesses in the DNS infrastructure to deceive users and compromise sensitive information. By implementing DNSSEC, domain owners can thwart these malicious activities, instilling confidence in their online visitors and fortifying their digital defenses against evolving threats.
Unlocking the Benefits of DNSSEC
1. Enhanced Security: DNSSEC adds an extra layer of protection to your online assets, reducing the risk of DNS-related attacks and ensuring the integrity of DNS data.
2. Improved Trustworthiness: By validating DNS responses, DNSSEC instills trust in your domain’s authenticity, fostering a positive user experience and bolstering your brand reputation.
3. Regulatory Compliance: With data privacy regulations tightening worldwide, DNSSEC compliance demonstrates your commitment to safeguarding user data and maintaining regulatory compliance.
4. Privacy: DNSSEC provides privacy protection by preventing attackers from seeing the domain names being queried by users.
The Anatomy of DNSSEC: How It Works
DNSSEC works by adding cryptographic signatures to existing DNS records to establish a secure DNS. The signatures get stored in DNS name servers alongside common record types, such as AAAA and MX. Then, by checking the signature that corresponds to a requested DNS record, you can verify that the record stems directly from its authoritative name server. This means that the record was never poisoned or otherwise tampered with during its digital transit — thereby preventing the introduction of fake records.
This process creates a chain of trust, from the root DNS servers down to the end-user’s device, ensuring the integrity of DNS data at every step.
Ready to harness the power of DNSSEC for your online presence?
In order to have DNSSEC enabled, registrars must have this technology enabled not only in their domain name infrastructure, but on the DNS server as well.
Some registrars support DNSSEC only when they act as the DNS server, and some others support both internal and external name servers.
Start by checking if your domain registrar and DNS hosting provider support DNSSEC. From there, follow a step-by-step implementation guide provided by your provider to enable DNSSEC for your domain. Remember, while the initial setup may require some effort, the long-term benefits of DNSSEC far outweigh the investment.
ICANN has an updated list of domain registrars who support DNSSEC, which includes some popular providers along with the supported TLDs. If you are using one of the registrars listed you will surely be able to secure your DNS records with DNSSEC.
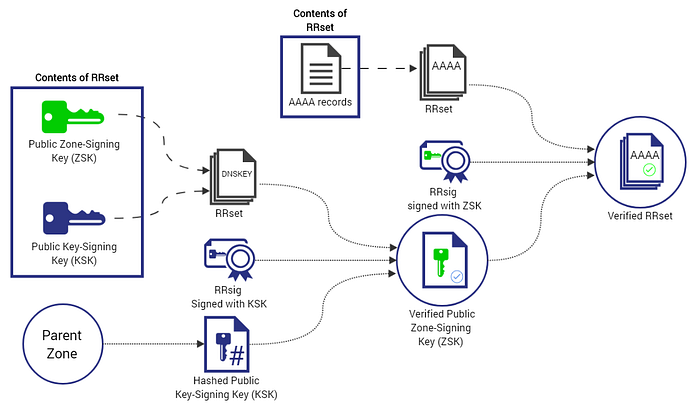
Depending on the situation, DNSSEC will add one of the following DNS record types to facilitate signature validation:
- Resource record signature (RRSIG): contains a cryptographic DNSSEC signature for a record set
- DNSKEY: contains a public signing key
- Delegation Signer (DS): contains the hash of a DNSKEY record
- Next Secure Record (NSEC and NSEC3): provides a link to the following record name in the zone, and also lists record types available for the record’s name
- CDNSKEY and CDS: conveys the requested DS state from the child zone to the parent zone, and requests updates to DS record(s) in the parent zone
When DNSSEC is used, each answer to a DNS request contains an RRSIG DNS record, in addition to the record type that was requested. The RRSIG record is a digital signature of the requested DNS data. The digital signature is verified by locating the correct public key that is found in the DNSKEY. The NSEC and NSEC3 records are used to provide cryptographic evidence of the non-existence of any request. This is also known as authenticated denial of existence.
The delegation signer (DS) is used in the authentication of DNSKEYs by using what is called a chain of trust. NSEC and NSEC3 also serve the purpose of providing robust resistance against spoofing.
 Credits : https://medium.com/iocscan/how-dnssec-works-9c652257be0
Credits : https://medium.com/iocscan/how-dnssec-works-9c652257be0
The chain of trust starts with a set of verified public keys for the DNS root zone which is the trusted third-party. Domain owners generate their own public key/private key pair and upload them using their DNS control panel at their domain-name registrar, which in term pushes the keys via secDNS to the zone operator (for example Verisign for the com zone) who signs and publishes them in the DNS
This prevents resolvers from caching forged or manipulated DNS data and prevents cache poisoning.
Conclusion:
As cyber threats continue to evolve, DNSSEC’s role in maintaining a trustworthy and secure internet becomes increasingly significant. Internet stakeholders, including domain registrars, DNS operators, and end-users, should continue to promote and support DNSSEC to enhance the overall security and resilience of the online ecosystem.
Its adoption and continuous development are essential for maintaining the integrity of the Domain Name System and preserving the foundation of our interconnected digital world.
So, why wait? Empower your domain with DNSSEC today and embark on a journey towards a more secure digital future!