
The content on this page was originally published on Instana.com and has been migrated to the community as a historical asset. As such, it may contain outdated information on our products and features. Please comment if you have questions about the content.
Service Level Indicators (SLI) and Service Level Objectives (SLO) are two important concepts in the field of observability. Both are used to measure the performance and availability of a service, but they have distinct purposes and are used in different ways.
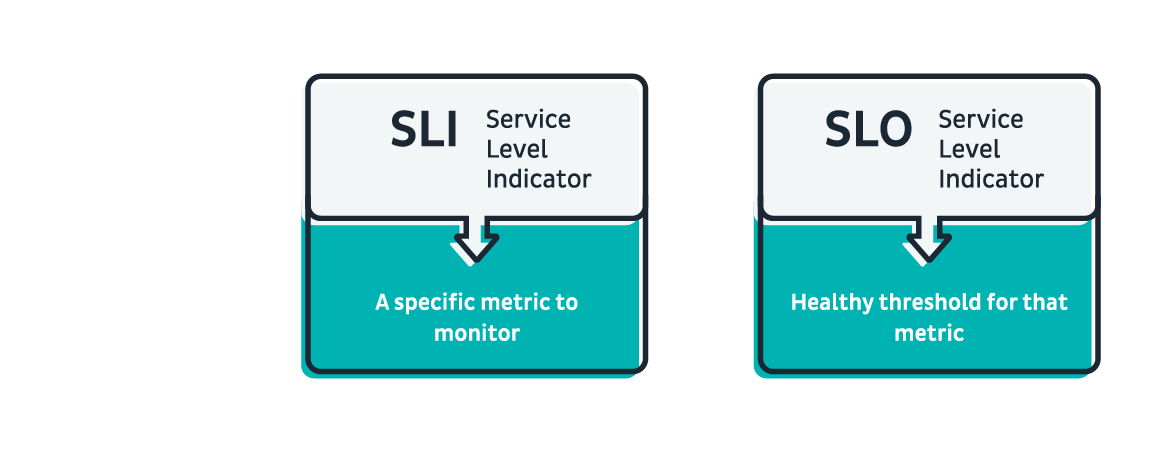
What is an SLI?

An SLI is a metric that is used to measure a specific aspect of a service’s performance. It is a numerical value that is collected and analyzed over time to provide insight into how well the service is functioning. Some examples of SLIs include response time, error rate, and throughput. These metrics are typically collected and analyzed using monitoring and logging tools.
You can also set up service-specific SLIs for some other measure of what “good performance” means. These SLIs generally fall into two categories:
- Request-based SLIs, where good service is measured by counting atomic units of service, like the number of successful HTTP requests.
- Windows-based SLIs, where good service is measured by counting the number of time periods, or windows, during which performance meets a goodness criterion, like response latency below a given threshold.
What is an SLO?

A Service Level Objective (SLO) is a target value or range of values for an SLI. It represents the desired level of performance for a service and is used to determine whether the service is meeting its performance goals. SLOs are typically expressed as a percentage or a range of values and are used to set targets for service performance. For example, a service might have an SLO of 99.9% uptime, meaning that it should be available 99.9% of the time.
Benefits of Implementing SLIs and SLOs
SLIs and SLOs are important tools for observability because they allow organizations to monitor the performance and availability of their services in a systematic and objective way. By setting SLOs and monitoring SLIs, organizations can identify problems with their services and take corrective action before they become critical.
Accurate Service Performance Measurements
One of the key benefits of using SLIs and SLOs for observability is that they provide a clear and objective way to measure service performance. This allows organizations to identify problems with their services quickly and take corrective action before they become critical.
Identify Trends in Service Performance
Another benefit of using SLIs and SLOs for observability is that they can be used to track the performance of a service over time. This allows organizations to identify trends and patterns in service performance, which can help them to identify and address issues more quickly.
Set Service Performance Targets
In addition, SLIs and SLOs can be used to set targets for service performance. This allows organizations to set goals for service performance and track progress towards achieving those goals. This is particularly useful for organizations that are looking to improve the performance of their services over time.
In practice, DevOps teams collect and analyze SLI and SLO data in order to measure the performance and availability of a service. This data is then used to identify problems with the service, such as slow response times, high error rates, or low throughput. Once these problems have been identified, the team can take corrective action to improve the service’s performance and availability.
For example, suppose a service’s response time is consistently slow. In that case, the observability team might investigate the cause of the slow response times, such as an overloaded database or a bottleneck in the network. Once the problem has been identified, the team can take corrective action, such as scaling up the database or adding more network capacity.
Another example is when an error rate is high, the observability team might investigate the cause of the high error rate and take action to fix the issue. This could include fixing bugs in the service’s code or making changes to the service’s architecture or infrastructure to reduce the number of errors.
It’s also important to note that when setting SLOs and monitoring SLIs, it’s important to consider the trade-offs between performance and availability. For example, increasing the number of servers to improve a service’s availability might also increase its response time. Therefore, it’s important to find the right balance between performance and availability that meets the needs of the service and its users.
In conclusion, Service Level Indicators (SLI) and Service Level Objectives (SLO) are critical concepts in observability. They provide a clear and objective way to measure service performance. Want to test drive instana SLO and SLI capability Play with Instana or sign up for a free, 14-day trial.
SLO Resources
To continue your journey on the path to understanding SLO and SLI Observability download below a resource: E-book on getting value from your SLIs and SLOs
